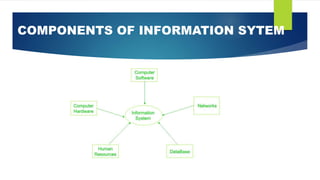
An information system combines hardware, software, networks, databases, and human resources to collect, create, and distribute useful data within an organization. The three core principles of information system security are confidentiality, integrity, and availability, known collectively as the CIA Triad. Confidentiality aims to keep information private, integrity ensures data is accurate and unaltered, and availability means systems and data are accessible when needed. Securing information systems protects against threats like hacking, cyberattacks, and data theft that could compromise confidential information or disrupt systems.