1. The document discusses network security goals such as protecting confidentiality, ensuring data integrity, and ensuring data availability.
2. It recommends planning for security which includes creating security policies and procedures, performing risk assessments, and ensuring adequate funding and staff training.
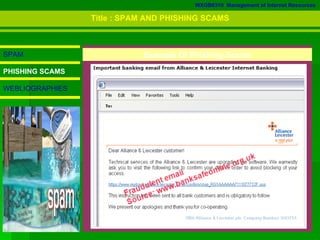
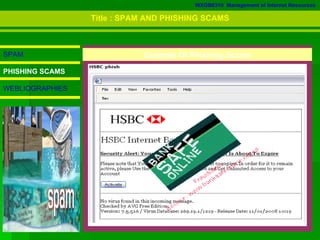
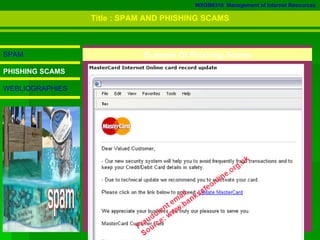
3. The document defines various types of malware like viruses, trojans, spyware, worms, and bots, and explains spam and phishing scams.