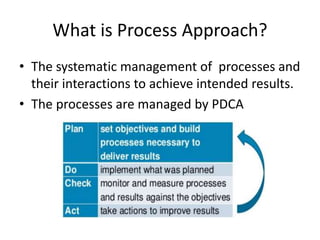
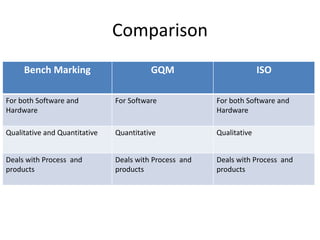
The document provides an overview of ISO standards, emphasizing their importance in improving organizational efficiency and communication. It details specific standards like ISO 9001 and ISO 25010, along with their applications and benefits, such as enhancing customer satisfaction and promoting international trade. Additionally, it includes case studies demonstrating the application of these standards in real-world scenarios for quality management.