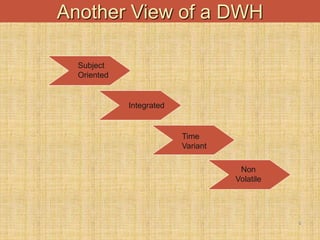
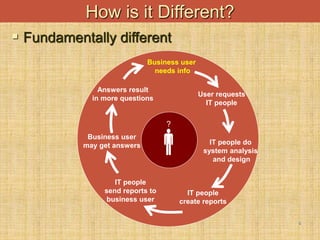
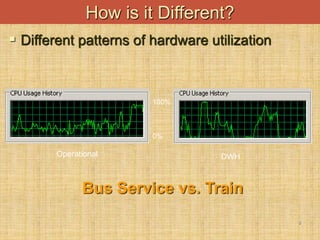
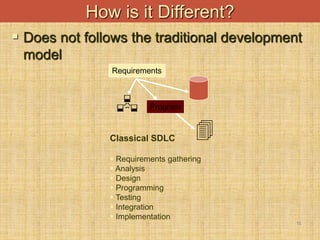
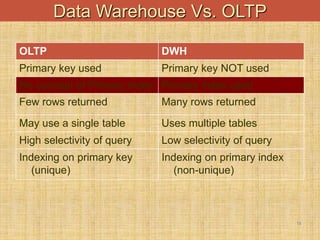
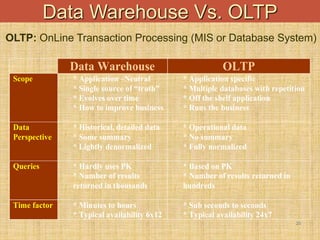
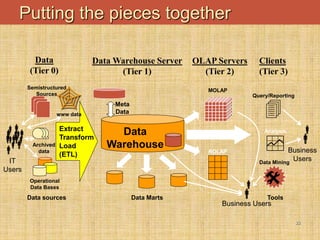
The document provides an introduction to data warehouses. It defines a data warehouse as a complete repository of historical corporate data extracted from transaction systems and made available for ad-hoc querying by knowledge workers. It discusses how data warehouses differ from transaction systems in integrating data from multiple sources, storing historical data, and supporting analysis rather than transactions. The document also compares characteristics of data warehousing to online transaction processing.