This document discusses negotiation and culture in international negotiations. It covers several key points:
1. It defines negotiation as an interactive process where parties seek mutually beneficial outcomes through joint decisions.
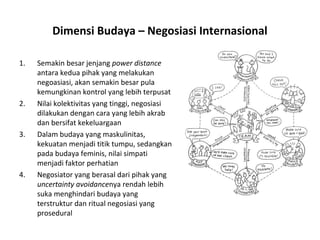
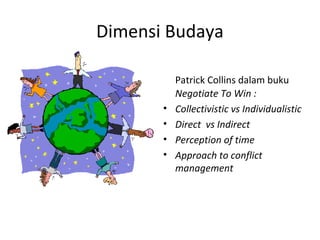
2. Culture influences negotiation through dimensions like power distance, individualism/collectivism, masculinity/femininity, and uncertainty avoidance.
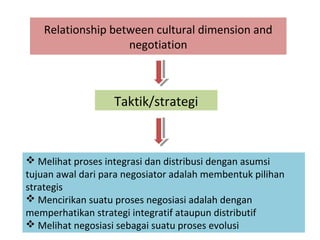
3. Cultural dimensions have implications for negotiation tactics - for example, high power distance cultures tend to have more centralized control in negotiations.
4. Understanding differences in interpersonal behaviors across cultures is essential for successful cross-cultural negotiation. Being aware of how culture shapes interaction styles is important.