1. Understanding cultural differences is essential for success in international business. Cultural differences can cause conflict but also promote good global business if understood.
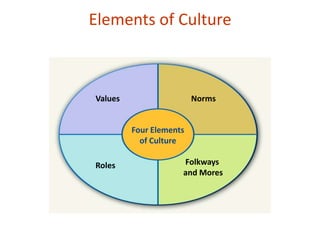
2. Culture refers to the beliefs, customs, and attitudes of a distinct group. There are national, regional, and local levels of culture that impact people's lives.
3. Succeeding in international business requires understanding culture, adjusting to culture, and participating in local culture.