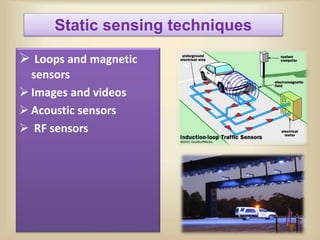
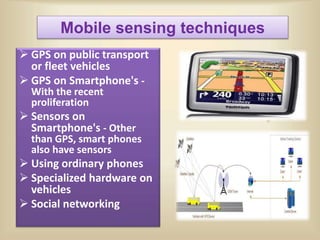
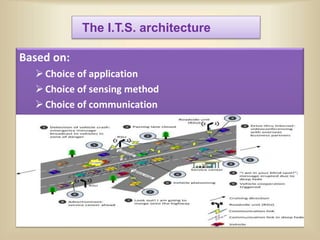
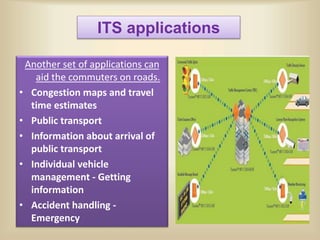
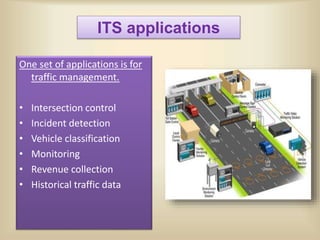
The document discusses intelligent transportation systems (ITS) which use technology to improve transportation efficiency and safety. ITS can sense traffic and road conditions using static sensors, mobile sensors in vehicles, or hybrid approaches. Sensing techniques include loops/magnetic sensors, images/videos, acoustic sensors, and RF sensors from static infrastructure, and GPS, smartphones, and specialized vehicle hardware for mobile sensing. ITS applications include traffic management, public transportation information, emergency management, and commercial vehicle monitoring to provide benefits like safety, productivity, and environmental performance. The document concludes that ITS could help address India's traffic congestion problems through evaluation and innovation of solutions.