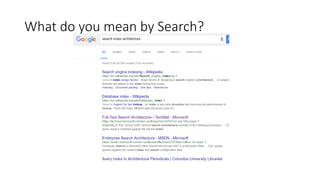
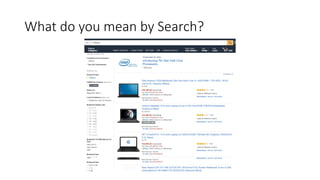
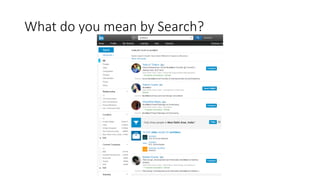
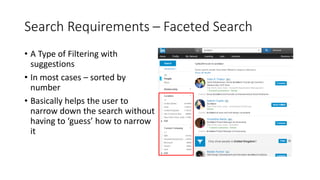
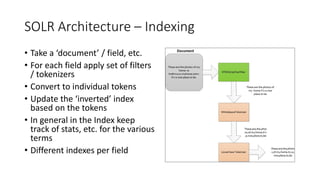
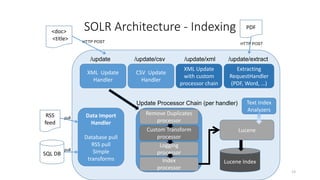
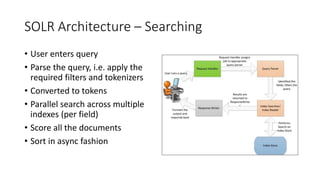
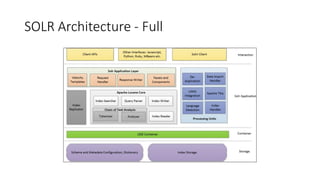
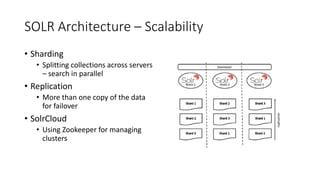
The document discusses the workings of Solr search, including its architecture, indexing, and comparison with SQL and NoSQL databases. It highlights various search requirements, advantages of Solr, and features like faceting, fuzzy matching, and scalability. Additionally, it covers how Solr is used in applications and compares it to other search technologies like Google Search and Elasticsearch.