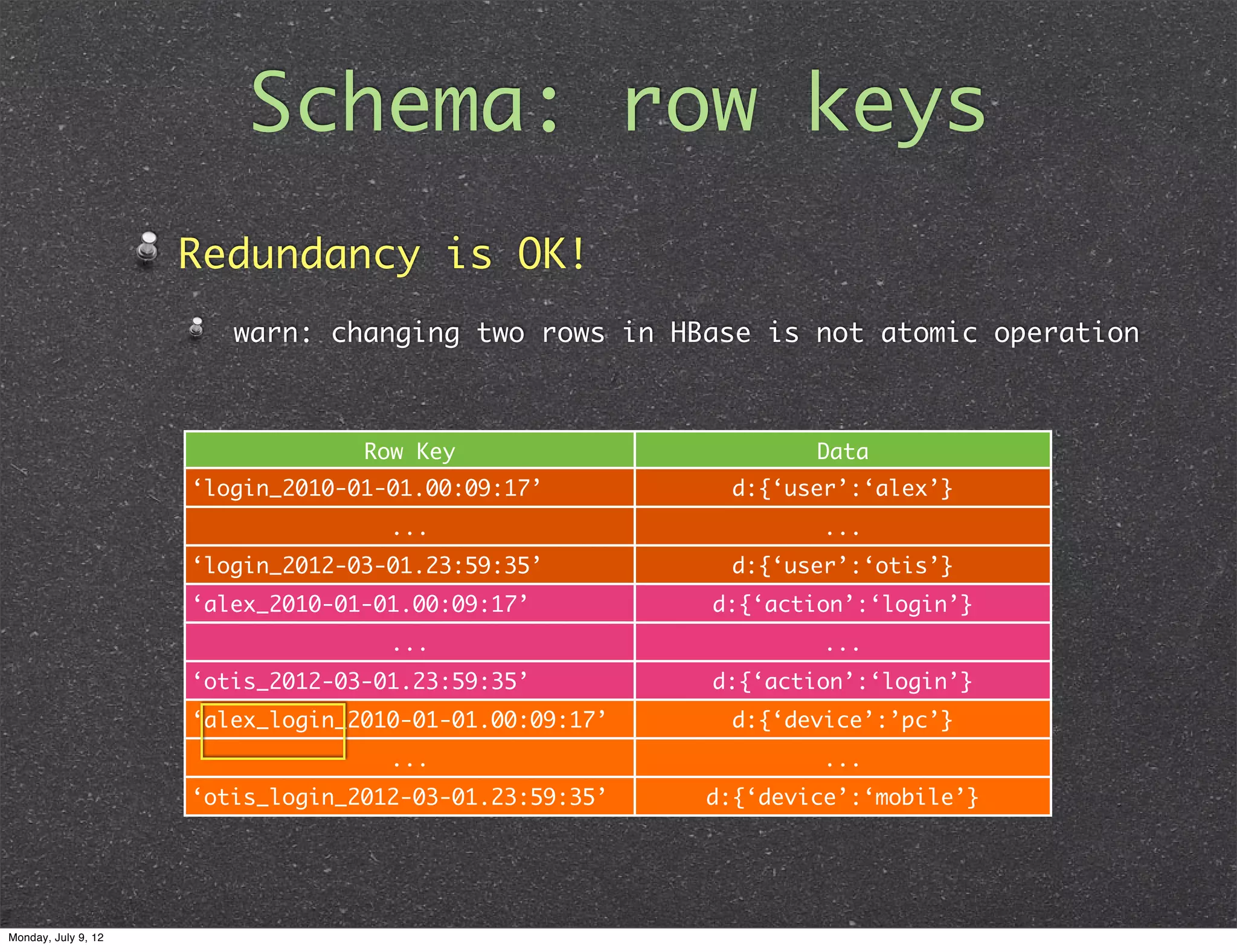
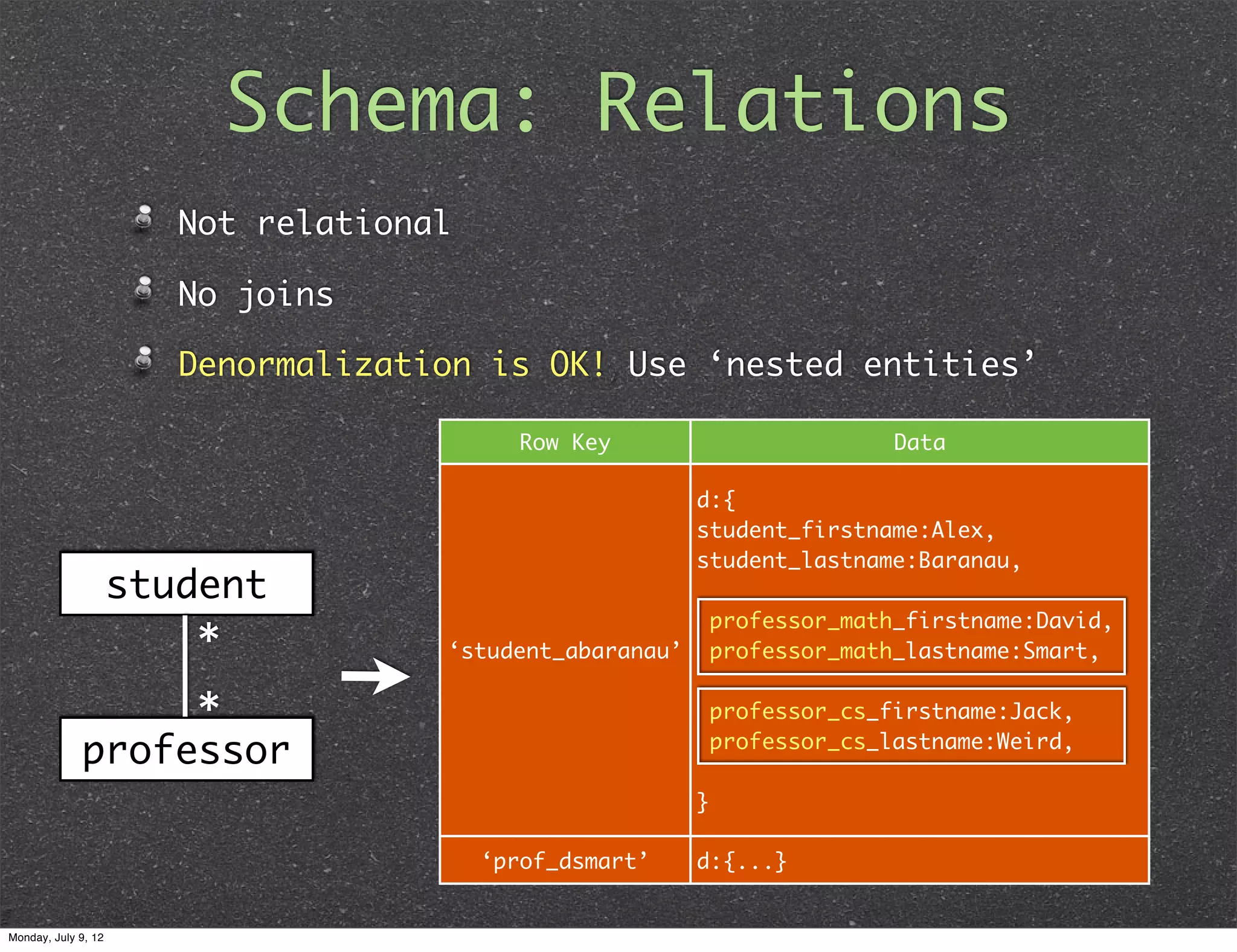
This document provides an introduction to HBase internals and schema design for HBase users. It discusses the logical and physical views of HBase, including how tables are split into regions and stored across region servers. It covers best practices for schema design, such as using row keys efficiently and avoiding redundancy. The document also briefly discusses advanced topics like coprocessors and compression. The overall goal is to help HBase users optimize performance and scalability based on its internal architecture.