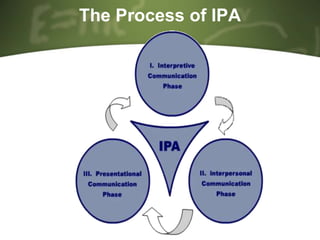
Integrated Performance Assessment (IPA) is a classroom-based assessment model that evaluates students' language skills in interpersonal, interpretive, and presentational modes. The IPA process begins with selecting a theme and corresponding tasks for each communicative mode. For example, with a food and nutrition theme, students might read about the food pyramid, discuss food diaries with partners, and present a daily food plan to the class. Choosing assessment activities requires defining the purpose and intended learning outcomes while ensuring students apply knowledge and skills through meaningful tasks.