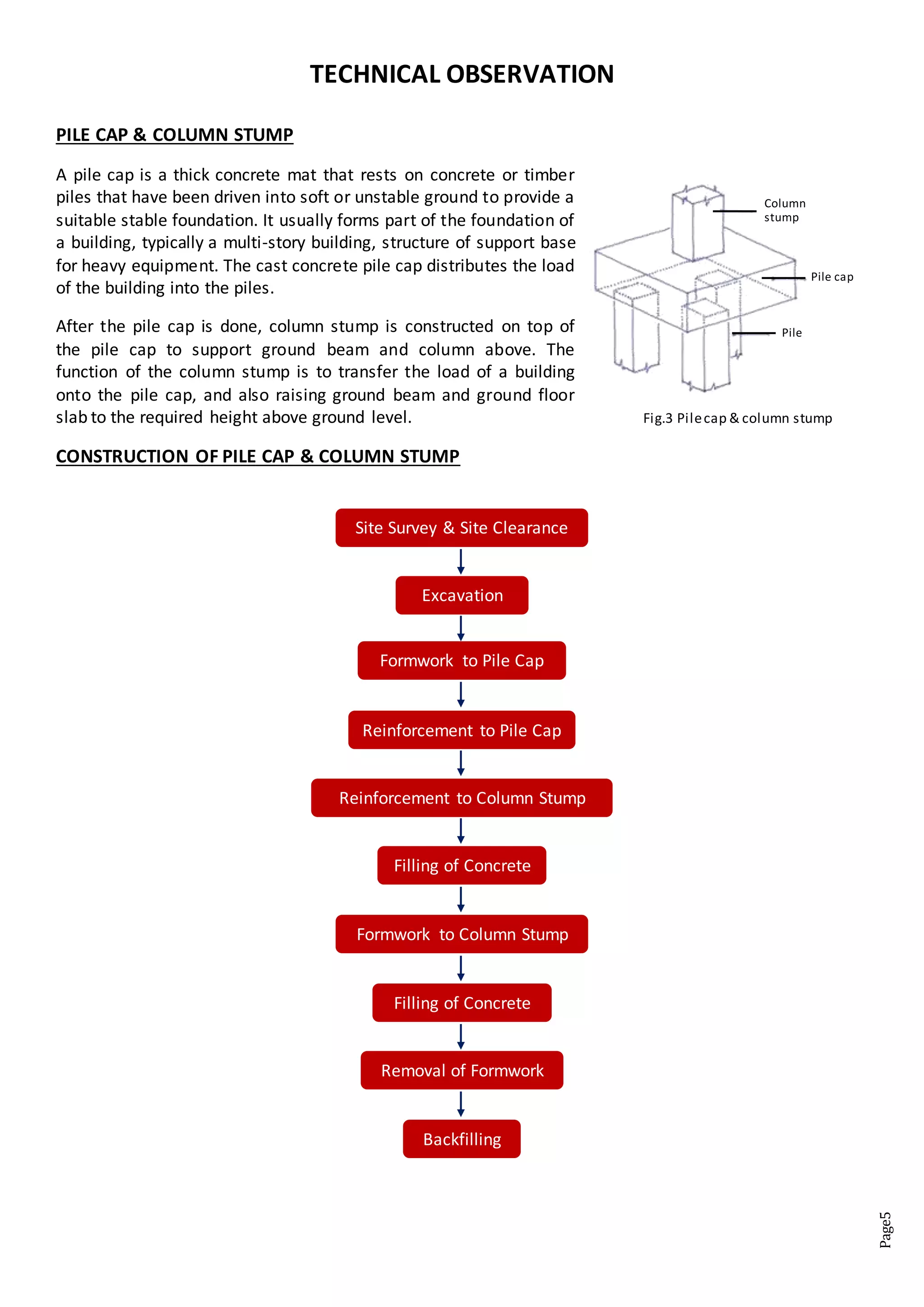
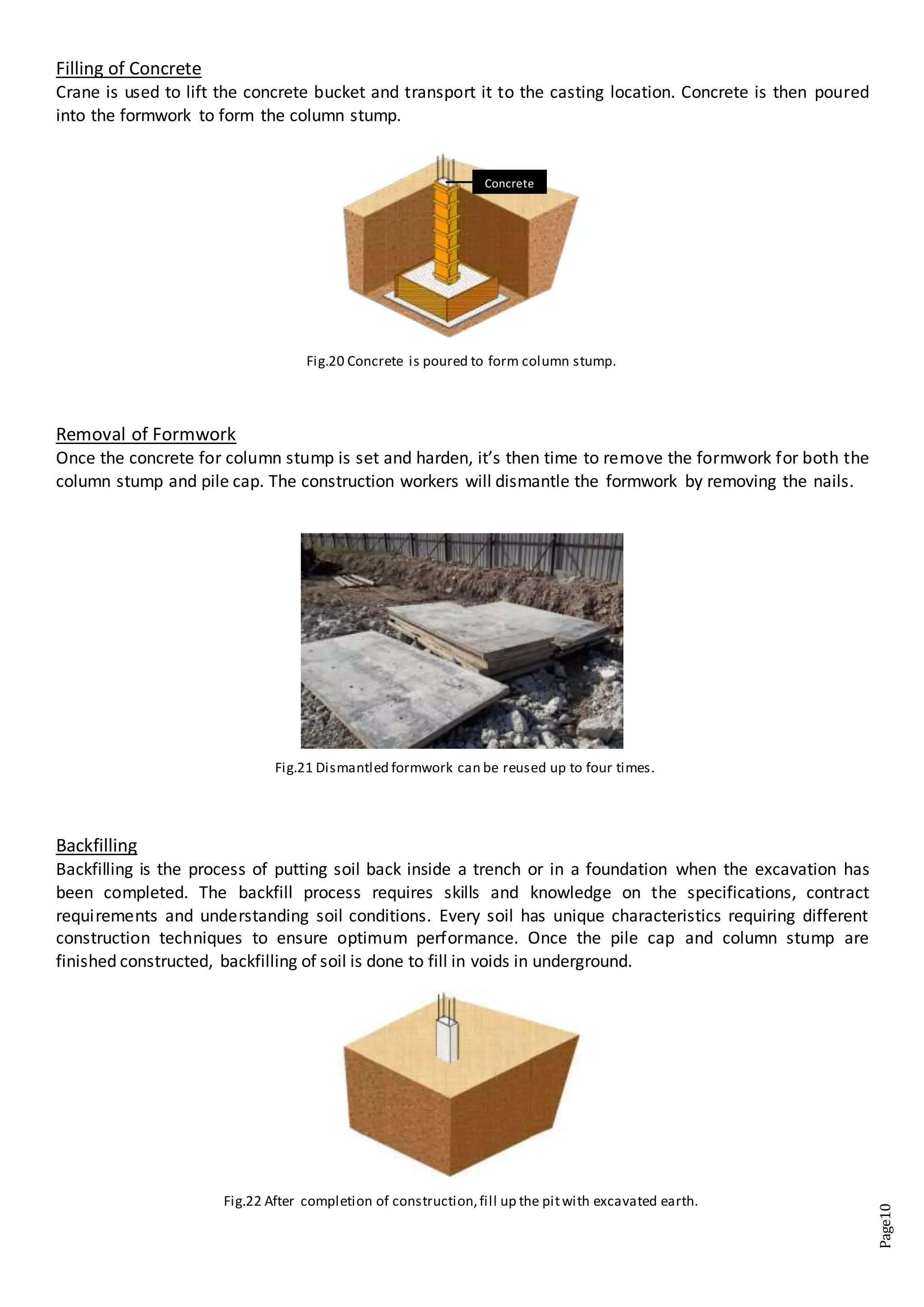
The document is a site visit report for a construction project building an apartment tower and car park. It includes an introduction describing the project and purpose of the site visit. The technical observation section describes the construction process for pile caps and column stumps including excavation, formwork, reinforcement, concrete pouring, and removal of formwork. Materials used like formwork, reinforcement, concrete spacers and concrete are also detailed. Photos in the appendix further illustrate the construction processes and components observed during the site visit.