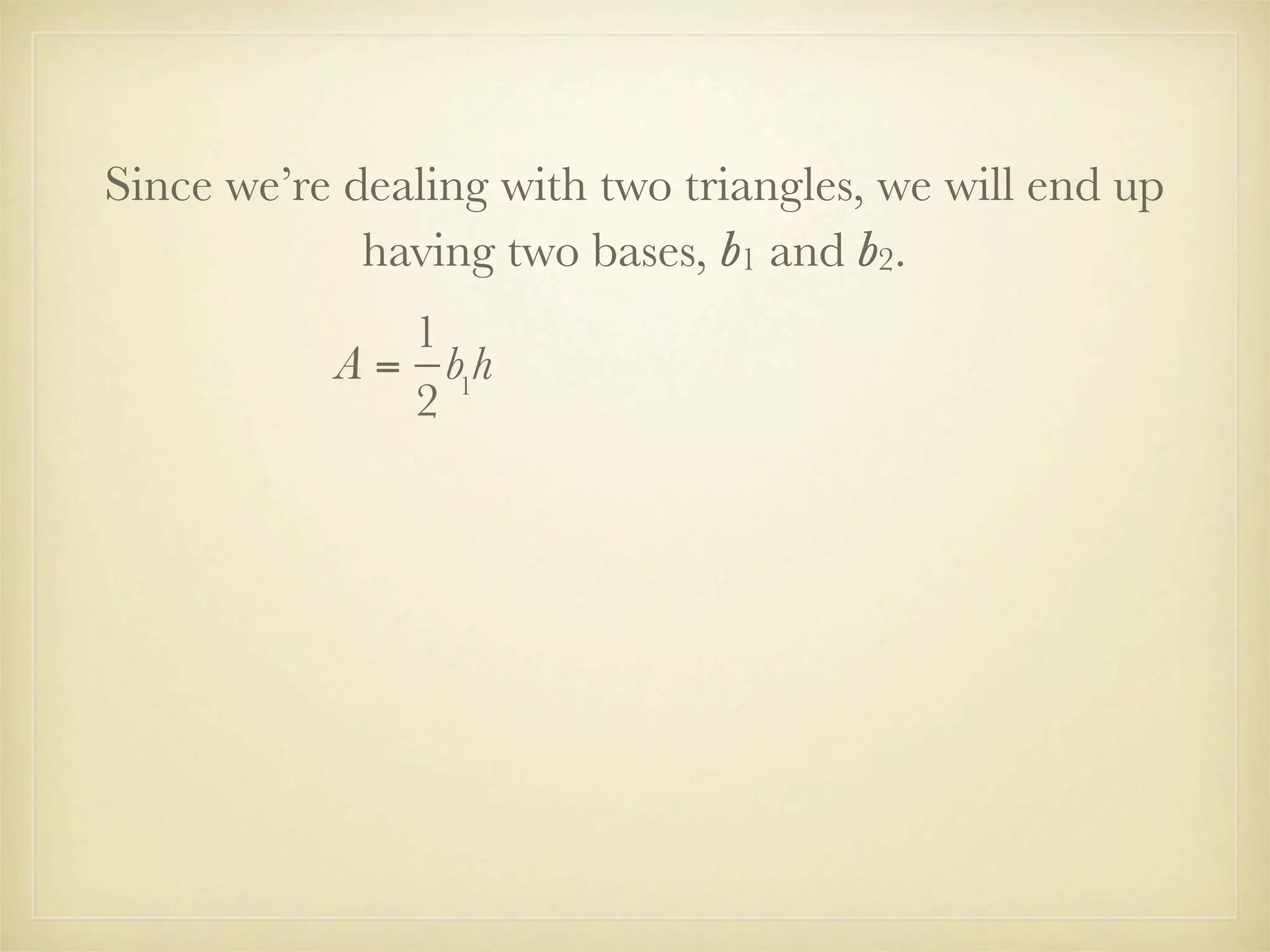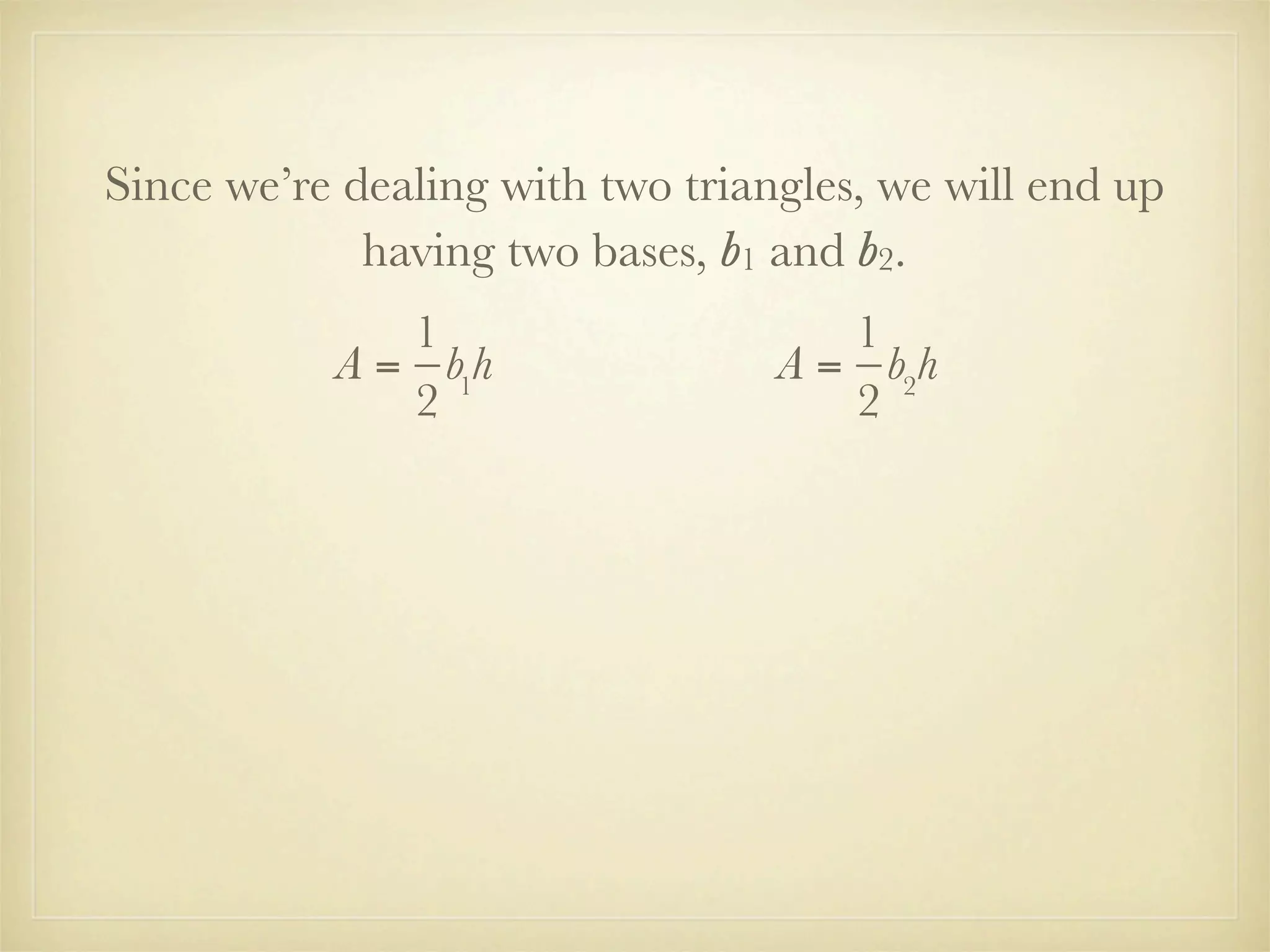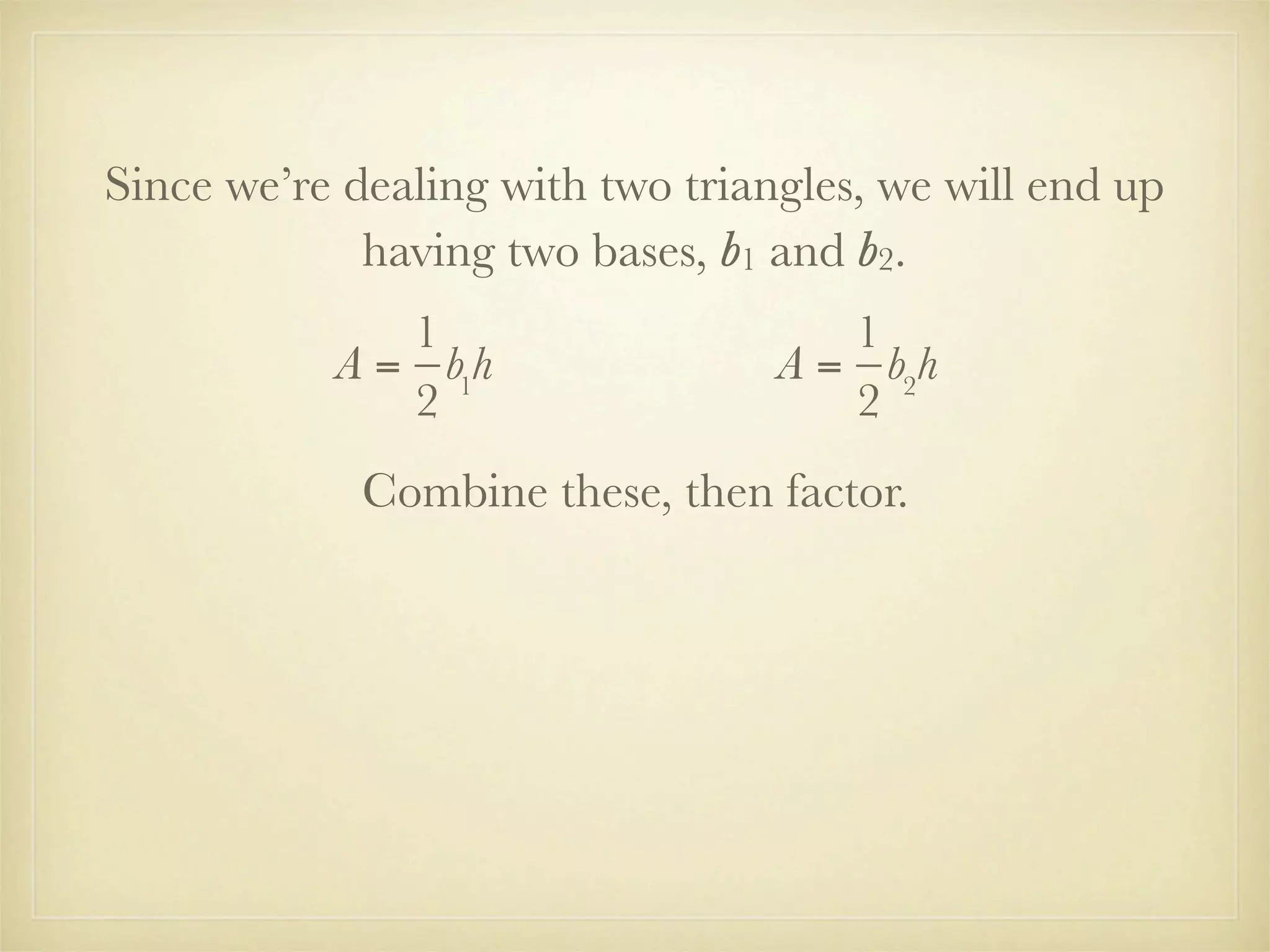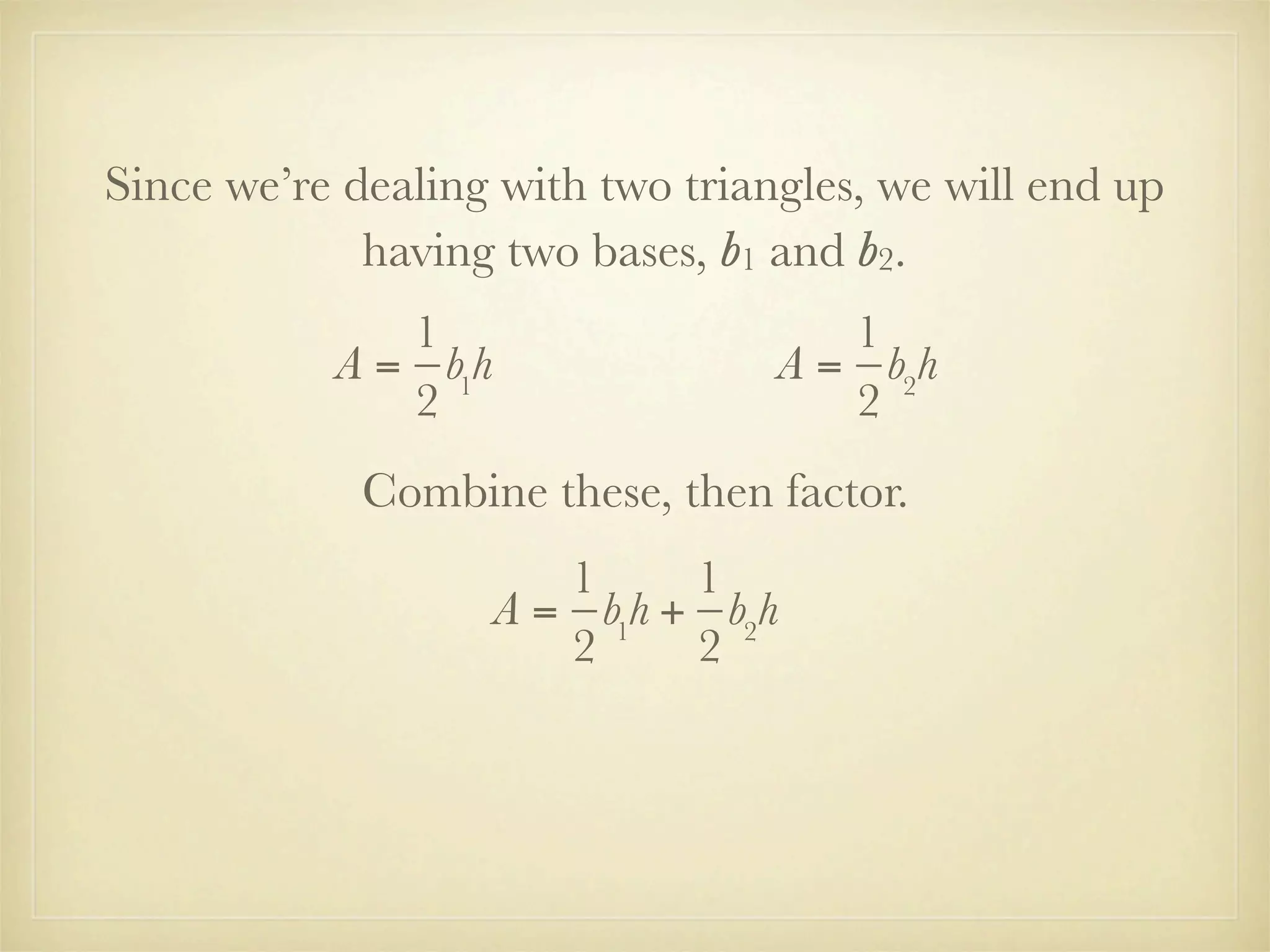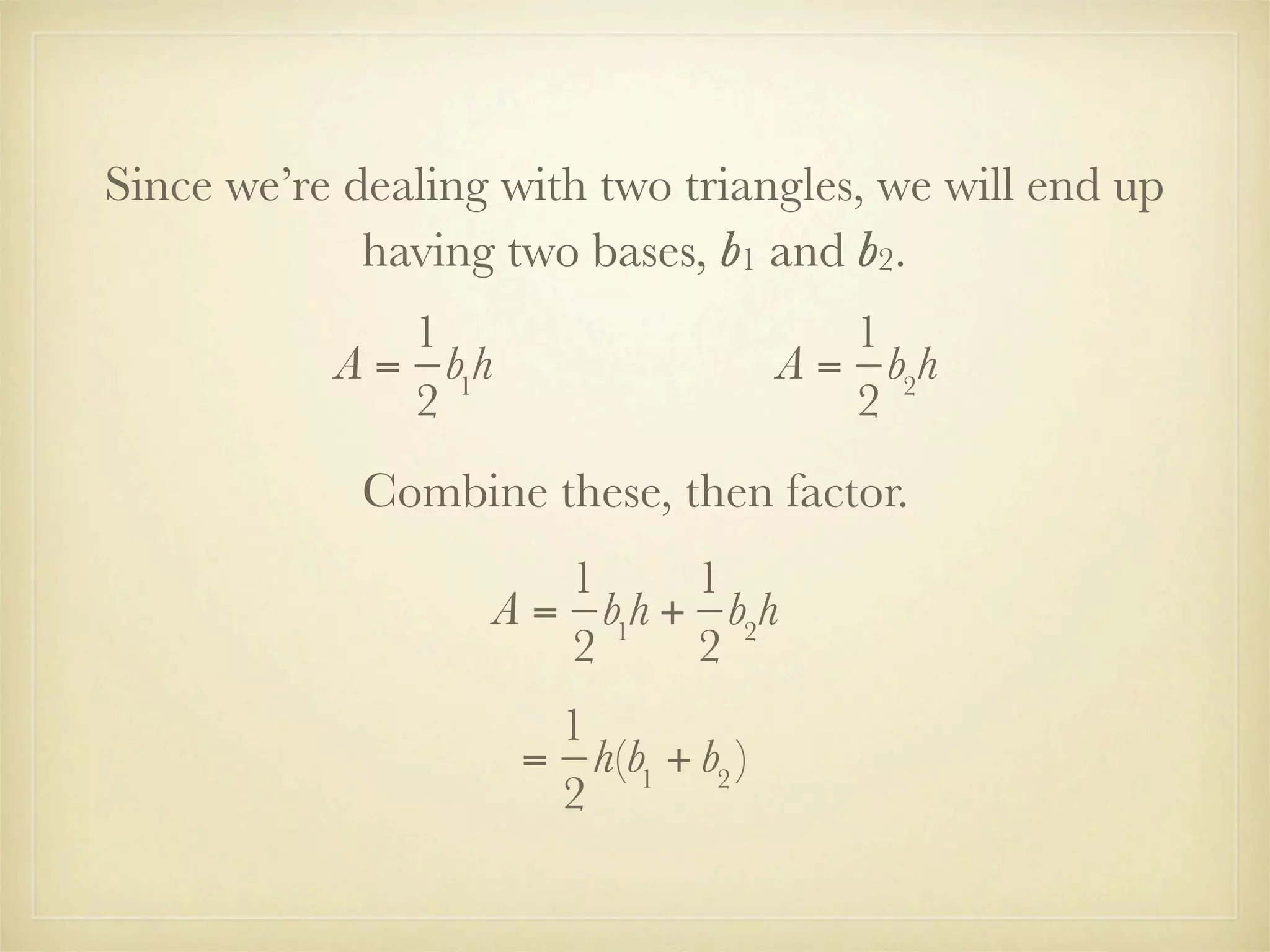This document provides instruction on factoring polynomials using the greatest common factor (GCF) method. It begins with an essential question and vocabulary definitions. It then walks through examples of factoring different polynomials step-by-step. The examples demonstrate finding the common factors of terms and variables and leaving the GCF outside parentheses. The document derives the formula for the area of a trapezoid and factors it out to show the process. It concludes with a problem set involving multiples of 3.