More Related Content
PPT
PPT
PPTX
PPTX
Section 13.5 special factoing techniques PDF
Math-8-Lesghdjkgdjkasjksghddgsjjkbxjksabson-2.pdf PDF
Factoring Polynomials in Modular Approach PPTX
MATHEMATICS8 Q1 9. solve problems involving special products and factors of p... PPTX
Similar to Polynomials and Functions aics9e_ppt_5_6.ppt
PPT
PPTX
0.5 Factoring Polynomials Factoring Polynomials.pptx PPT
PDF
PDF
DOCX
1st Quarter MATH 8 module PPT
PPTX
PPTX
G8 Math Q1- Week 1-2 Special Products and Factors (1).pptx PPTX
Special Products and Factors.pptx PPTX
MATH 8 Q1 LESSON 5-special products for binomials, and factorization of polyn... PPTX
Math 8-LesGBSGHSWsonHAKDOGMAUPRTS 2.pptx PPTX
MATHEMATICS8 Q1 8. completely factor different types of polynomials (polynomi... PPT
098A_exponents_factoring.ppt PPT
098A_exponents_factoring.ppt PPTX
Lecture 03 special products and factoring PPTX
PPT
PPT
PPTX
Q1-W1-Factoring Polynomials.pptx More from SalgieSernal2
PPTX
mathematicalsystem-definedandundefinedterms-230228135055-48e0ae47.pptx PPTX
628952927-Illustrating-Rational-Algebraic-Expressions.pptx PPTX
368844469-Rational-Algebraic-Expressions.pptx PPTX
lesson-7-factorising-using-the-difference-of-two-squares.pptx PPT
MAthematics 522331894-G7-MATH-Sets-WEEK-1.ppt PPT
07-sets.ppt MATHEMATIcs 7 all about sets and suset PPTX
PPT_Prepare_a_variety_of_sandwiches_FN_060114.pptx PPTX
Science 429482364-MATERIALS-THAT-BENT.pptx PPT
MAthematics 7 356665408-Introduction-to-Sets.ppt PPTX
381001213-5-Alokasyon-at-Sistemang-Pang-ekonomiya.pptx PPT
mathematics 424403333-SETS-Presentation-ppt.ppt PPT
Factoring polynomials ch13powerpoint.ppt PPTX
THE-HUMAN-PERSON-IN-THE-ENVIRONMENT.pptx PPTX
introductiontophilosophyofthehumanperson-220824121629-9957eefb.pptx PPTX
Part of the brain, function of the brain PPTX
HUMAN PERSON AS AN EMBODIED presentationSPIRIT.pptx PPTX
METHODS-OF-PHILOSOPHIZING-ppt-presentation PPTX
FLS Powerpoint Presentation POWER POINT PRESENTATION PPTX
BE LCP-SALGIE power point presentation for learning purposes PPTX
BE LCP- Educational purposes only SALGIE.pptx Recently uploaded
PPTX
How to Manage Line Discounts in Odoo 18 POS PDF
Unit-III pdf (Basic listening Skill, Effective Writing Communication & Writin... PPTX
Kochi MuleSoftMeetup_UnlockingMCPServer.pptx PPTX
Pain. definition, causes, factor influencing pain & pain assessment.pptx PPTX
How to Manage Reception Report in Odoo 18 Inventory PPTX
Pig- piggy bank in Big Data Analytics.ppt.pptx PDF
NAVIGATE PHARMACY CAREER OPPORTUNITIES.pdf PPTX
PURPOSIVE SAMPLING IN EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH RACHITHRA RK.pptx PDF
Projecte de la porta de la classe de primer A: Mar i cel. PDF
Models of Teaching - TNTEU - B.Ed I Semester - Teaching and Learning - BD1TL ... PPTX
Basics in Phytochemistry, Extraction, Isolation methods, Characterisation etc. PDF
IMANI Africa files RTI request seeking full disclosure on 2026 SIM registrati... PPTX
Filipino 11-Tekstong Prosidyural-Final.pptx PDF
Projecte de la porta de primer B: L'antic Egipte PDF
All Students Workshop 25 Yoga Wellness by LDMMIA PPTX
Details of Epithelial and Connective Tissue.pptx PDF
M.Sc. Nonchordates Complete Syllabus PPT | All Important Topics Covered PPTX
The Cell & Cell Cycle-detailed structure and function of organelles.pptx PPTX
Searching in PubMed andCochrane_Practical Presentation.pptx PDF
Analyzing the data of your initial survey Polynomials and Functions aics9e_ppt_5_6.ppt
- 1.
1
Copyright © 2015,2011, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 5-1
Polynomials
and Polynomial
Functions
Chapter 5
- 2.
2
Copyright © 2015,2011, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 5-2
5.1 – Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials
5.2 – Multiplication of Polynomials
5.3 – Division of Polynomials and Synthetic
Division
5.4 – Factoring a Monomial from a Polynomial
and Factoring by Grouping
5.5 – Factoring Trinomials
5.6 – Special Factoring Formulas
5.7-A General Review of Factoring
5.8- Polynomial Equations
Chapter Sections
- 3.
3
Copyright © 2015,2011, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 5-3
§ 5.6
Special Factoring
Formulas
- 4.
4
Copyright © 2015,2011, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 5-4
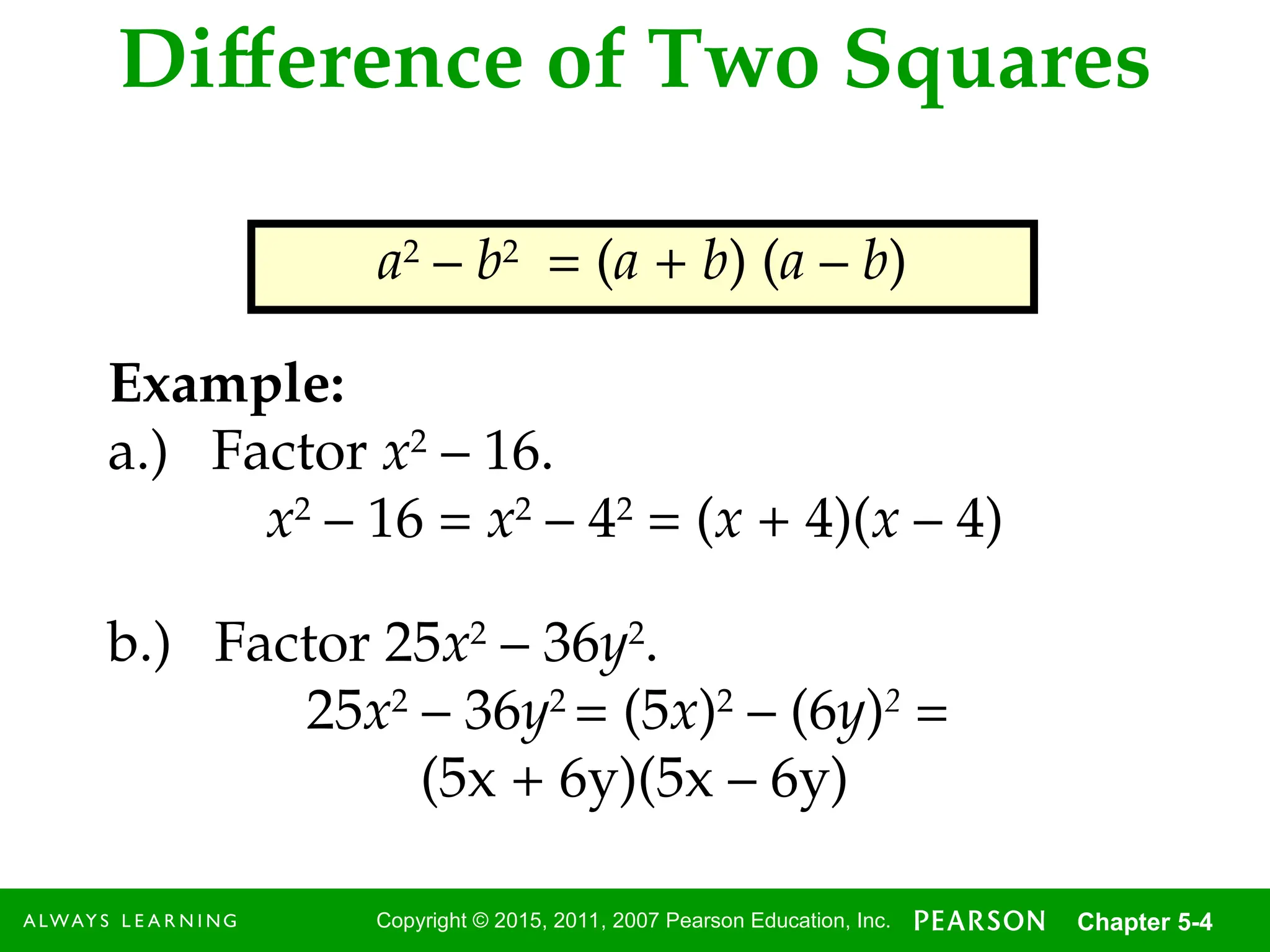
Difference of Two Squares
a2
– b2
= (a + b) (a – b)
Example:
a.) Factor x2
– 16.
x2
– 16 = x2
– 42
= (x + 4)(x – 4)
b.) Factor 25x2
– 36y2
.
25x2
– 36y2
= (5x)2
– (6y)2
=
(5x + 6y)(5x – 6y)
- 5.
5
Copyright © 2015,2011, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 5-5
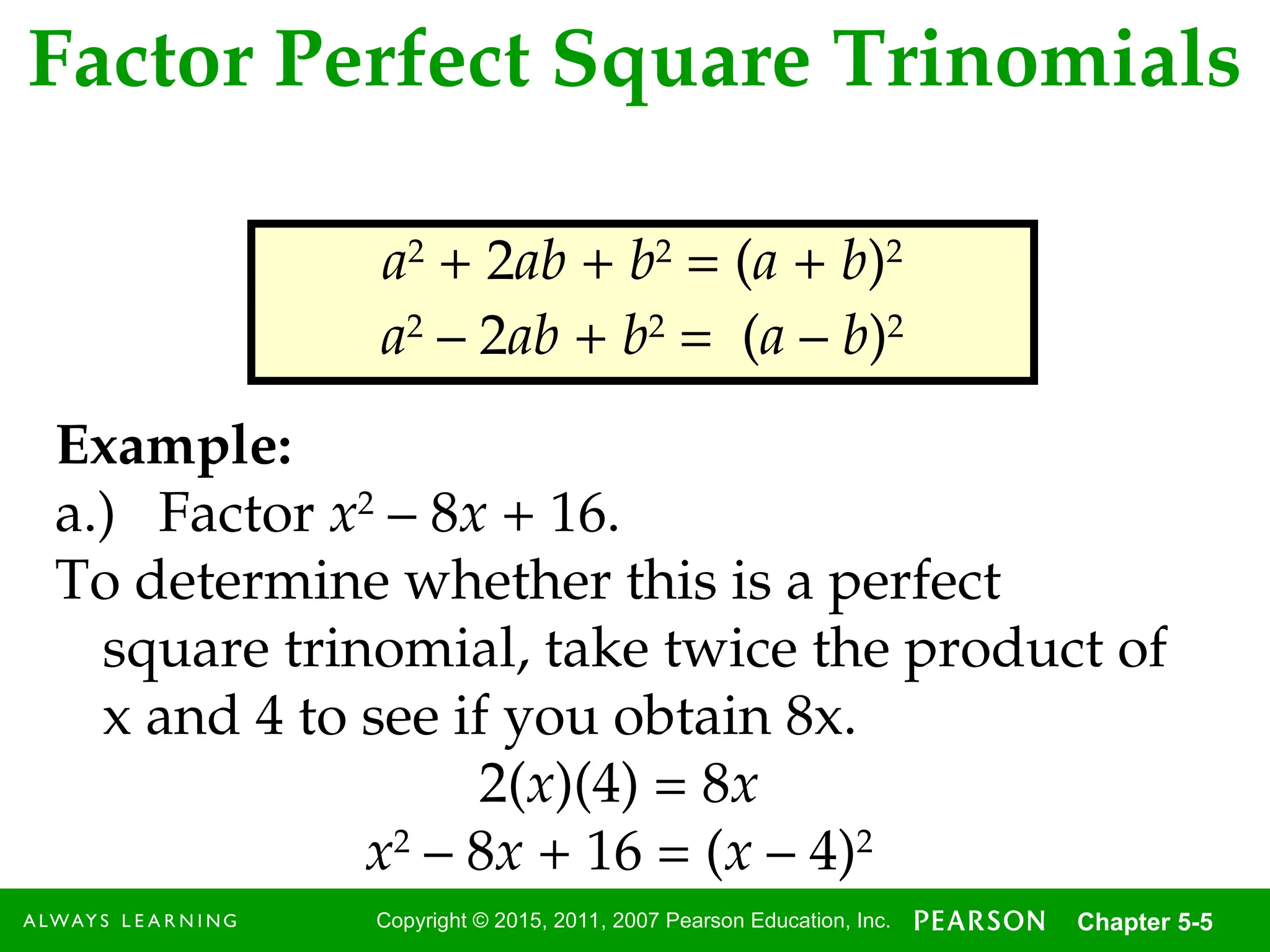
Factor Perfect Square Trinomials
a2
+ 2ab + b2
= (a + b)2
a2
– 2ab + b2
= (a – b)2
Example:
a.) Factor x2
– 8x + 16.
To determine whether this is a perfect
square trinomial, take twice the product of
x and 4 to see if you obtain 8x.
2(x)(4) = 8x
x2
– 8x + 16 = (x – 4)2
- 6.
6
Copyright © 2015,2011, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 5-6
Sum of Two Cubes
a3
+ b3
= (a + b) (a2
– ab + b2
)
Example:
a.) Factor the sum of cubes x3
+ 64.
)
16
4
)(
4
(
]
4
)
4
(
)[
4
(
4
)
)(
(
2
2
2
3
3
2
2
3
3
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
b
ab
a
b
a
b
a
- 7.
7
Copyright © 2015,2011, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 5-7
Difference of Two Cubes
a3
– b3
= (a – b) (a2
+ ab + b2
)
Example:
a.) Factor 27x3
– 8y6
.
)
4
6
9
)(
2
3
(
]
)
2
(
)
2
)(
3
(
)
3
)[(
2
3
(
)
2
(
)
3
(
8
27
4
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
3
2
3
6
3
y
xy
x
y
x
y
y
x
x
y
x
y
x
y
x
- 8.
8
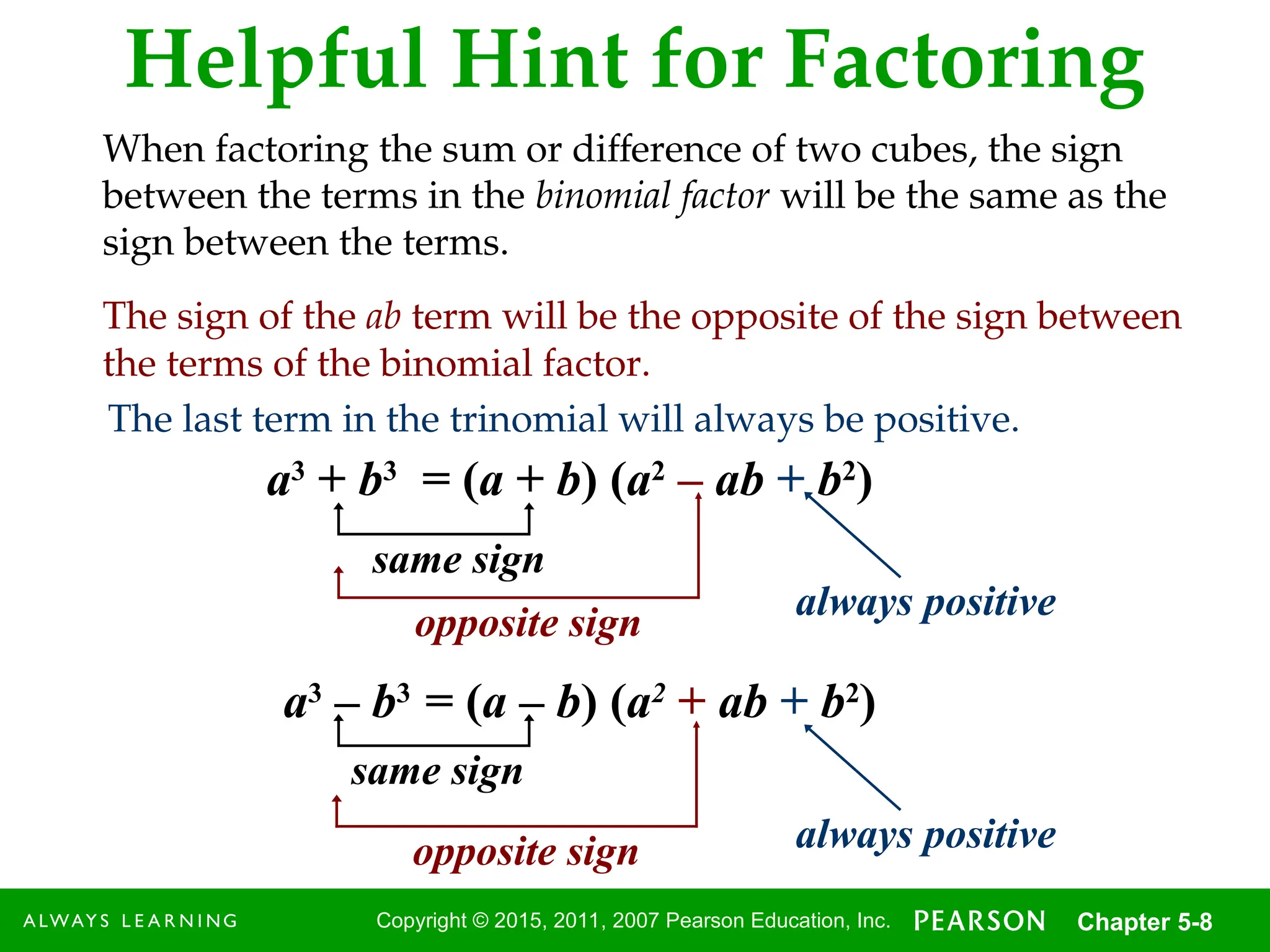
Copyright © 2015,2011, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 5-8
Helpful Hint for Factoring
When factoring the sum or difference of two cubes, the sign
between the terms in the binomial factor will be the same as the
sign between the terms.
The sign of the ab term will be the opposite of the sign between
the terms of the binomial factor.
a3
+ b3
= (a + b) (a2
– ab + b2
)
same sign
The last term in the trinomial will always be positive.
a3
– b3
= (a – b) (a2
+ ab + b2
)
same sign
opposite sign
always positive
opposite sign always positive



![6
Copyright © 2015, 2011, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 5-6
Sum of Two Cubes
a3
+ b3
= (a + b) (a2
– ab + b2
)
Example:
a.) Factor the sum of cubes x3
+ 64.
)
16
4
)(
4
(
]
4
)
4
(
)[
4
(
4
)
)(
(
2
2
2
3
3
2
2
3
3
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
b
ab
a
b
a
b
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aics9eppt56-250918021329-efafab5c/75/Polynomials-and-Functions-aics9e_ppt_5_6-ppt-6-2048.jpg)
![7
Copyright © 2015, 2011, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 5-7
Difference of Two Cubes
a3
– b3
= (a – b) (a2
+ ab + b2
)
Example:
a.) Factor 27x3
– 8y6
.
)
4
6
9
)(
2
3
(
]
)
2
(
)
2
)(
3
(
)
3
)[(
2
3
(
)
2
(
)
3
(
8
27
4
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
3
2
3
6
3
y
xy
x
y
x
y
y
x
x
y
x
y
x
y
x
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aics9eppt56-250918021329-efafab5c/75/Polynomials-and-Functions-aics9e_ppt_5_6-ppt-7-2048.jpg)