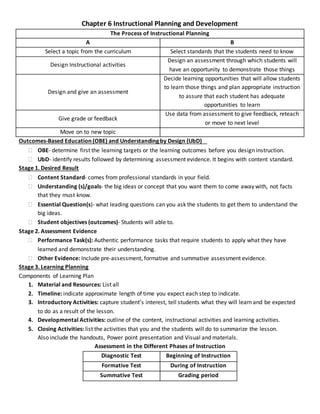
The document discusses instructional planning and lesson plan development. It describes several models for instructional planning including the process of instructional planning, outcomes-based education, and Understanding by Design. It also outlines the key elements and components of effective lesson plans, such as setting objectives and outcomes, designing assessments, and incorporating instructional activities. Various instructional strategies like direct and indirect instruction are also mentioned. Overall, the document provides an overview of different approaches to instructional planning and the essential parts of high-quality lesson plans.