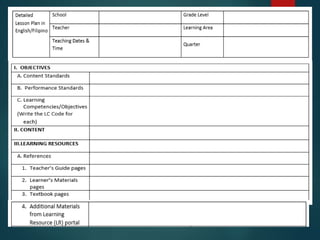
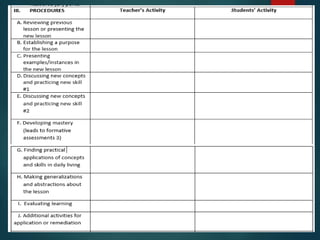
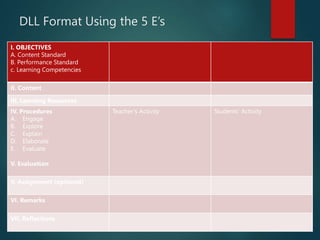
This document outlines the importance of lesson planning for teachers. It discusses the key elements that should be included in a lesson plan such as learning objectives, instructional strategies, and assessment. A lesson plan should follow the curriculum standards and guide learning through an introduction, body, and conclusion. Lesson planning is necessary to effectively facilitate learning in the classroom and ensure students are able to meet expected outcomes.