This document outlines steps for systematic instructional planning including:
1) Identifying instructional goals and analyzing learners.
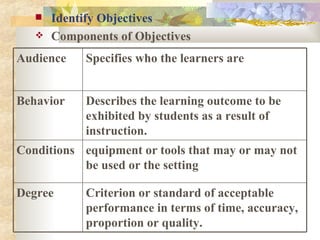
2) Identifying objectives which specify learning outcomes, conditions, and audience. Objectives can be cognitive, affective, or psychomotor.
3) Planning instructional activities such as introducing objectives, presenting content, and providing practice.
4) Choosing appropriate instructional media.
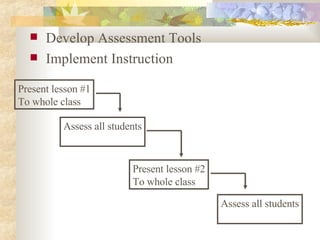
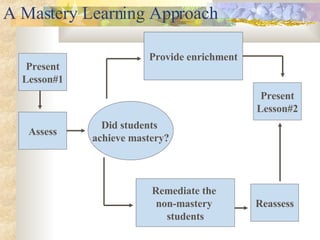
5) Developing assessment tools and implementing a mastery learning approach through presentation, assessment, and revision.