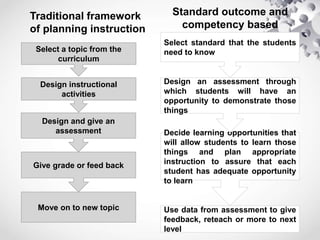
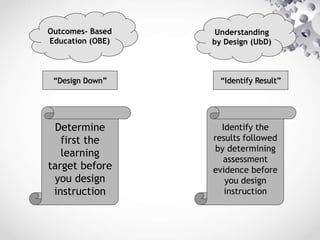
The document outlines a comprehensive framework for instructional planning and development, emphasizing a backward design approach through stages of desired results, assessment evidence, and learning plans. It details the components of lesson plans and effective strategies for instructional methods, including both deductive and inductive teaching. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of aligning instruction with desired outcomes and providing opportunities for student reflection and self-assessment.