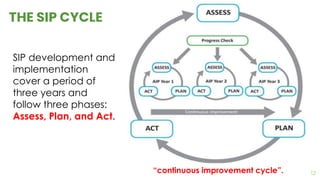
This document discusses institutional planning in education. It defines institutional planning as a program of development and improvement prepared by an educational institution based on its needs and available resources, with the goal of improving practices. The objectives of institutional planning are to impart realism to educational planning, develop comprehensive improvement programs utilizing optimal resources, and align institutional development with national planning. The document outlines the scope, importance, nature, and stakeholders involved in institutional planning. It emphasizes institutional planning as a continuous cycle of assessment, planning, and action.