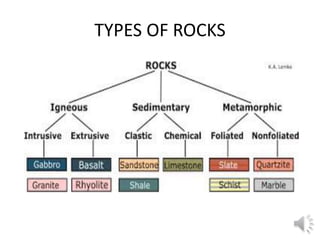
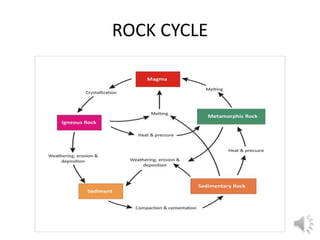
The document summarizes key details about the structure and composition of the Earth's interior. It describes how the Earth can be divided into three main layers - the crust, mantle, and core. The crust is the solid outermost layer and is made up of either continental or oceanic crust. Below the crust is the mantle, which extends to a depth of 2,900 km and is composed of dense materials like iron and magnesium. The core is at the center of the Earth and is made of heavy metals like nickel and iron, with temperatures reaching over 5,000°C.



![CRUST-
Solid outermost layer
Also known as lithosphere
Continental crust(35km thick)
[SiAl]
Oceanic crust(5km thick) [SiMa]
Average density- 3.0 g per cubic
cm
MANTLE-
Layer beneath crust
2900km thick
Made of dense and heavy materials
such as iron and magnesium
Average density ranges between 3.5g
to 5.5 g per cubic cm
Magma is found in this layer
CORE-
Also known as barysphere
Average radius is about 3500km
Made of heavy metals such as
nickel and iron [NiFe]
Temperature varies from 2200 to
5000⁰C
Average density ranges between
5.0g and 13.0g per cubic cm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insideourearth-211212064212/85/Inside-our-earth-4-320.jpg)