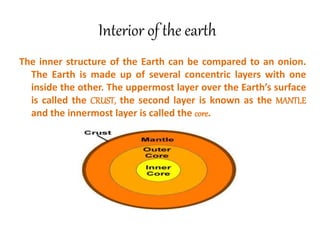
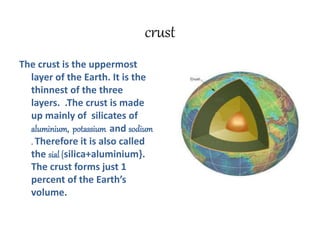
The document discusses the interior structure of the Earth. It is composed of three main layers - the crust, mantle, and core. The crust is the outermost layer and thinnest, made up of silicates. Below is the thick mantle layer, divided into upper and lower sections. The innermost layer is the core, made of iron and nickel. Rocks form the crust and are made of minerals - the basic building blocks. There are three main types of rocks: igneous formed from cooled magma, sedimentary formed from compressed sediments, and metamorphic formed from changes to pre-existing rocks under heat and pressure.