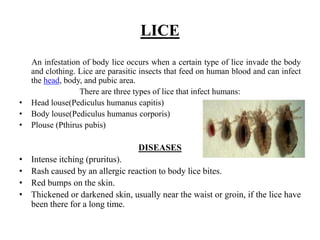
This document provides information on insect, vector and rodent control. It discusses spiders, flies, ticks, mites, lice and fleas, describing each pest and the diseases they can transmit. For each pest, it outlines symptoms of related diseases and recommends methods of control, such as removing ticks promptly, applying pesticides, reducing habitats, and practicing good sanitation and hygiene. The overall goal is to educate the public and minimize disease transmission by controlling these vectors.