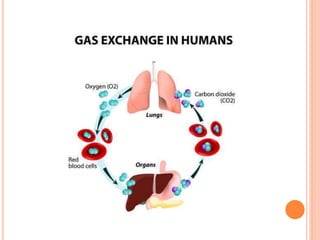
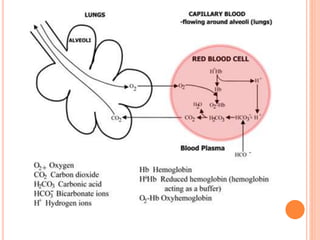
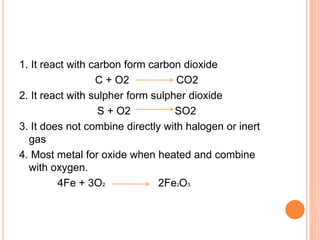
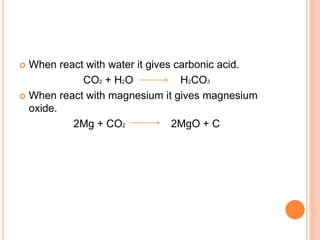
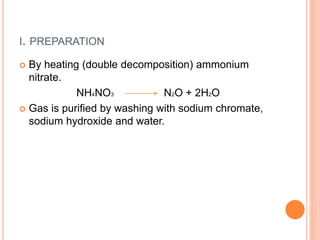
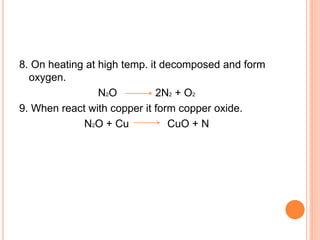
This document discusses three common inhalants: oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrous oxide. It provides details on their formulas, preparation methods, properties, actions and uses, and storage. Oxygen is prepared by fractionation of air or electrolysis of water. It is colorless, odorless, and tasteless. Carbon dioxide is prepared by burning carbon-containing materials or treating carbonates with acid. It is colorless and odorless with an acidic taste. Nitrous oxide is prepared by heating ammonium nitrate and is also known as laughing gas.