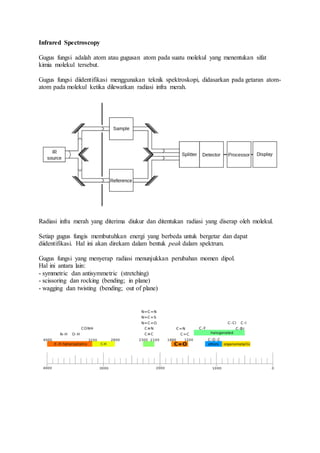
Infrared spectroscopy can be used to identify functional groups in molecules based on the vibrational energies of atoms in the molecule when exposed to infrared radiation. Each functional group requires a different energy to vibrate, which causes it to absorb infrared radiation at characteristic wavelengths. The intensity of these absorption peaks indicates the strength of the vibration and can be used to identify functional groups present in an unknown sample.