This document provides information about information gathering and tools that can be used for information gathering. It discusses gathering information from existing sources and examples to understand issues and how others have addressed them. The document also describes the Maltego tool which can be used to gather and represent information in a meaningful way by identifying relationships. Finally, it outlines the Nmap security scanning tool, its objectives, functions, and how it can be used to map networks and discover hosts and open ports.

















![Intense Discovery!
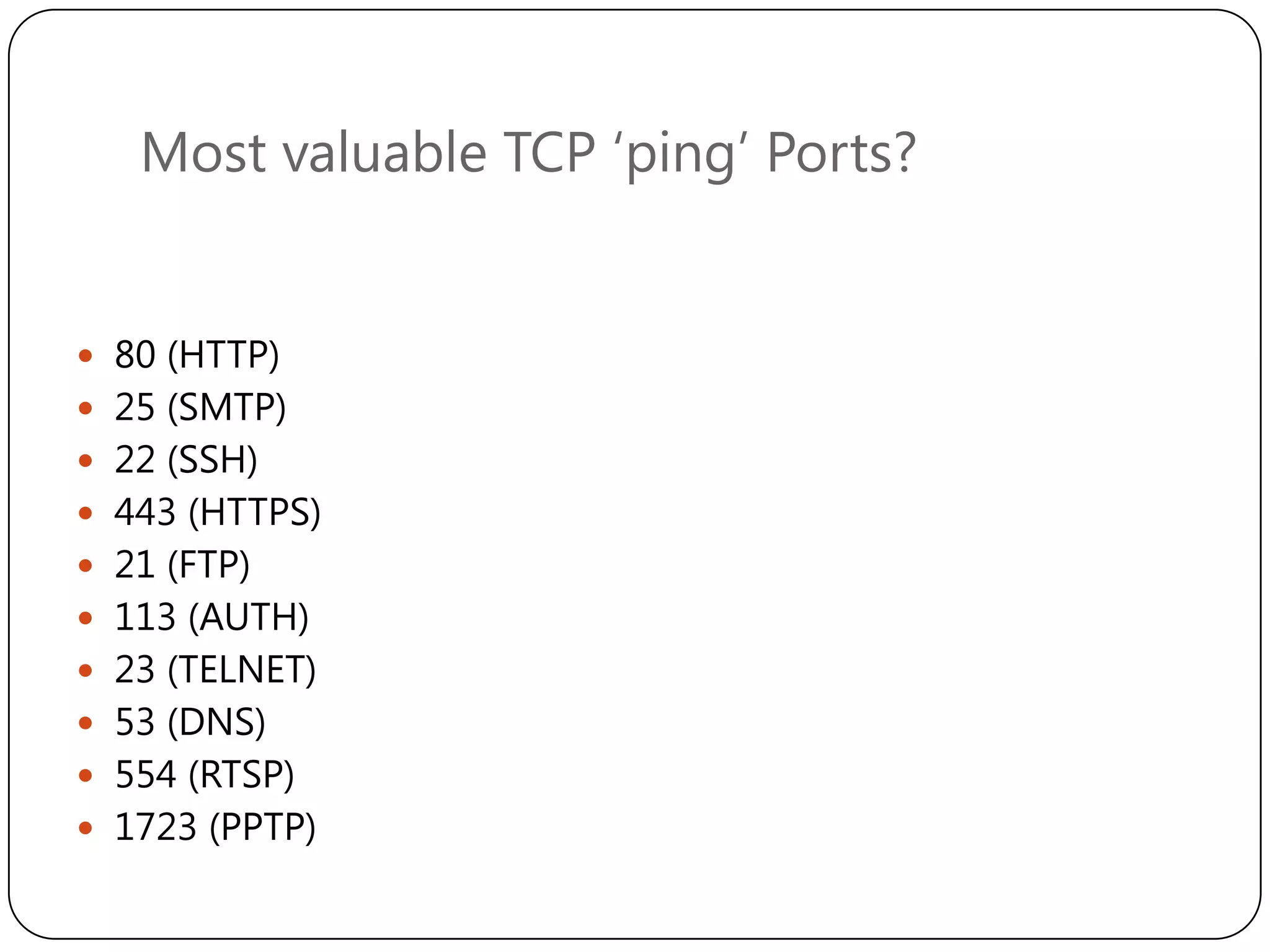
# nmap –sP –PE –PP –PS21,22,23,25,80,113,21339
–PA80,113,443,10042 –source-port 53 –n
–T4 –iR 10000
[ … lots of IPs … ]
Host a.b.c.d appears to be up.
Host w.x.y.z appears to be up.
Nmap finished: 10000 IP addresses (699 hosts up) scanned
in 2016.564 seconds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationgathering-140215012535-phpapp01/75/Information-gathering-20-2048.jpg)

