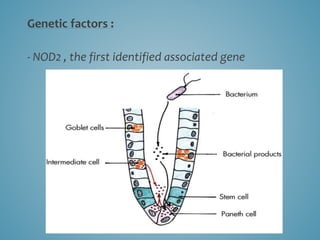
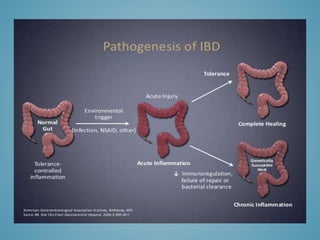
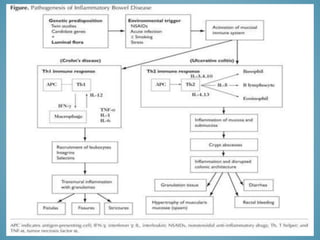
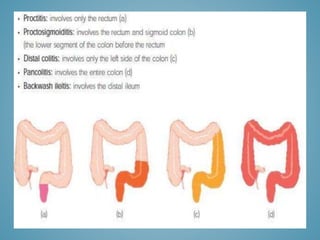
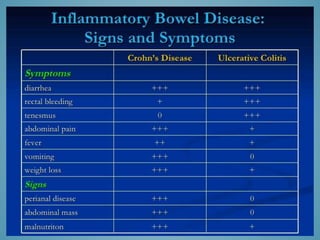
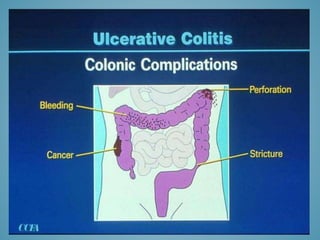
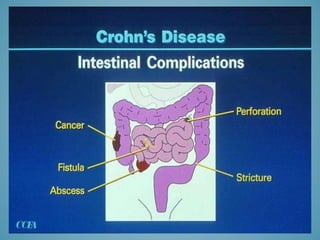
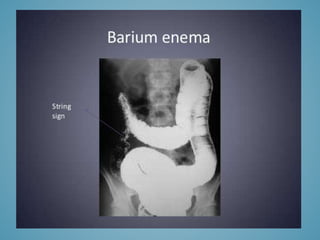
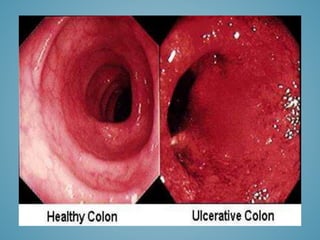
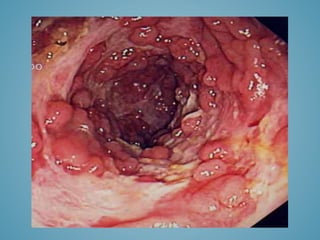
This document provides information on inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). IBD includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, which are characterized by chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract. The causes are poorly understood but involve genetic, immunological, and environmental factors. Crohn's disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, while ulcerative colitis only affects the colon. Treatment involves medications to control symptoms, with surgery as an option for severe or treatment-resistant cases. Medical treatments include aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and anti-TNF antibodies. Diet therapies are also used for Crohn's disease.