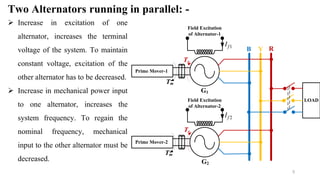
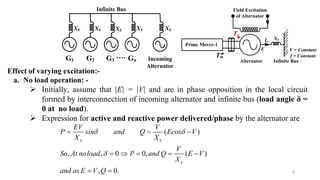
This document discusses an alternator connected to an infinite bus. It defines an infinite bus as a constant voltage and frequency source that can absorb or supply reactive power without changing its characteristics. The document explains that at no load, an alternator synchronized to an infinite bus is in a floating condition where it delivers or absorbs no real or reactive power. It then describes what happens when the alternator's excitation is increased or decreased. An increase leads to reactive power delivery, while a decrease leads to reactive power absorption from the infinite bus, as the alternator's emf changes relative to the bus voltage. In both cases, an armature current is established to maintain the alternator's constant air-gap flux.