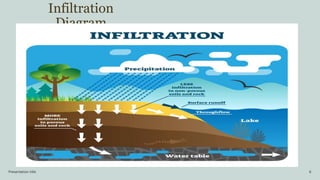
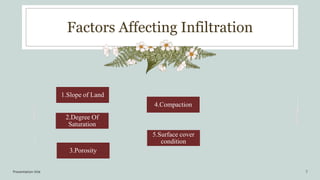
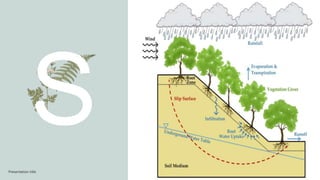
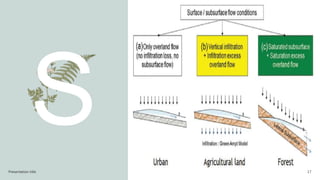
This document discusses infiltration, which is defined as the flow of water from aboveground into the subsurface. It receives attention due to its importance for topics like irrigation, contaminant transport, groundwater recharge, and ecosystem viability. The document outlines factors that affect infiltration rates, including slope, degree of saturation, porosity, compaction, and surface cover conditions. Steeper slopes, higher saturation, lower porosity, greater compaction, and impermeable surface covers can decrease infiltration rates.