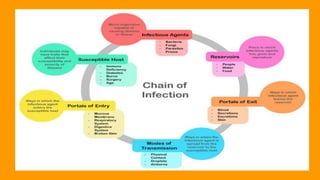
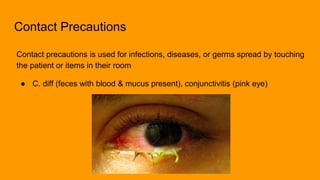
This document discusses infection prevention and control. It defines infections, how they spread, and common pathogens. It emphasizes that proper handwashing and following standard precautions are critical to preventing the spread of infections. It also outlines different types of precautions like airborne, droplet, and contact precautions that are used depending on the infection. Special precautions are needed for multidrug-resistant organisms and bloodborne pathogens.