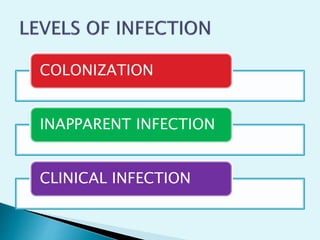
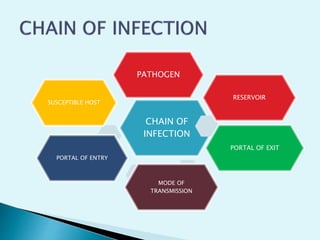
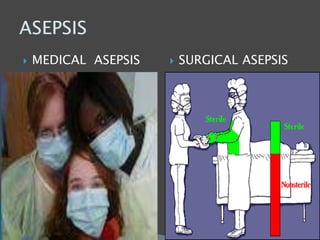
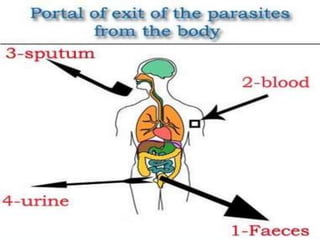
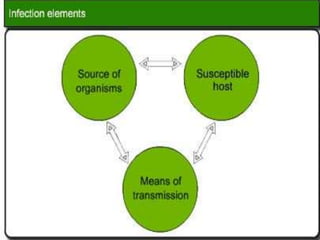
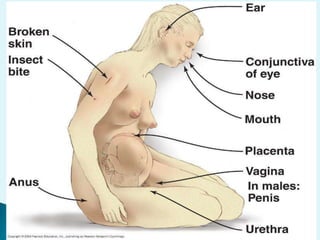
The document discusses various aspects of infection control and safety in a healthcare setting. It defines infection and different types of infections. It outlines the chain of infection and methods for controlling reservoirs and transmission of pathogens like cleansing, asepsis, disinfection and sterilization. It also discusses personal protective equipment, biomedical waste management categories, sharps safety, and various measures to ensure patient and staff safety in the physical environment.