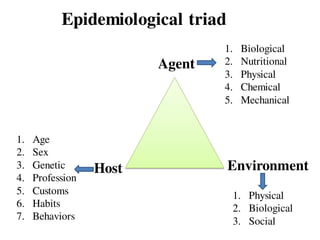
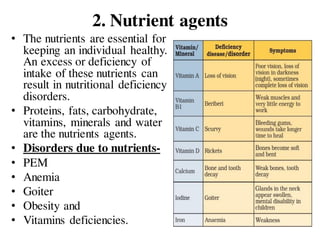
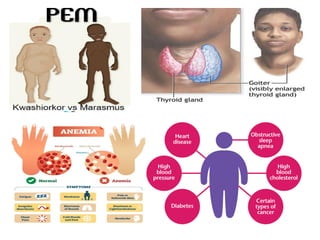
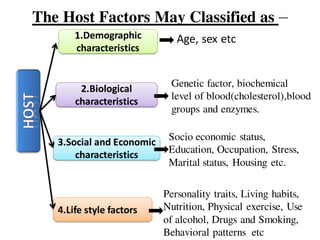
The document discusses the epidemiological triad, which consists of three essential factors for disease occurrence: agent, host, and environment. It details various types of disease agents, including biological, nutritional, chemical, mechanical, physical, and social agents, as well as host factors like demographics and lifestyle. Finally, it examines environmental factors that contribute to diseases, categorizing them into physical, biological, and physiological environments.