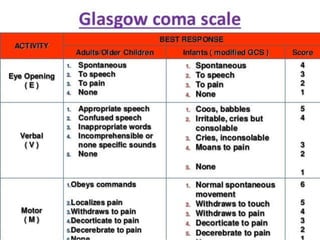
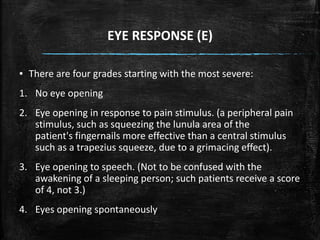
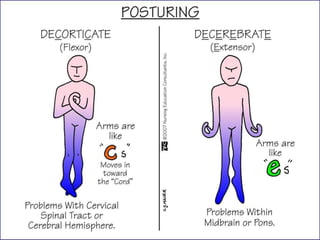
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), developed in 1974, assesses a patient's consciousness through eye, verbal, and motor responses, scoring between 3 (deep unconsciousness) to 15 (full consciousness). It helps classify brain injuries as severe (GCS < 8-9), moderate (GCS 8-12), or minor (GCS ≥ 13), although limitations exist for cases involving tracheal intubation and young children. The documentation provides detailed scoring criteria for the three components and their interpretations.