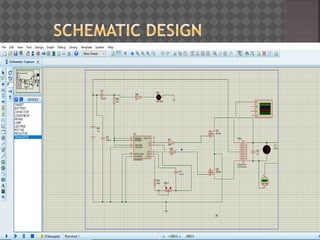
The document discusses the design and working principles of an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). It details the components involved in the inverter circuit, including MOSFETs, batteries, capacitors, and ICs, as well as their function and applications. The document concludes with the successful simulation of the inverter design using Proteus software and cites several references for further reading.