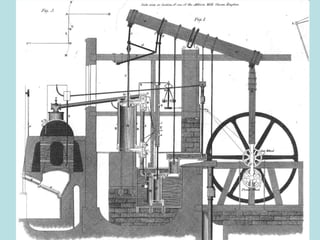
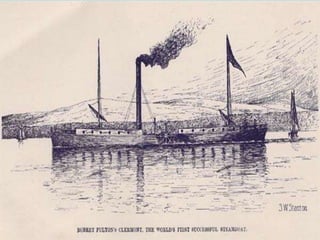
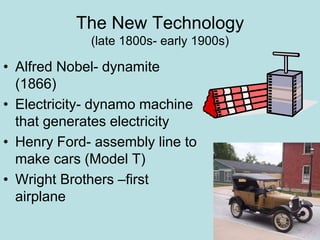
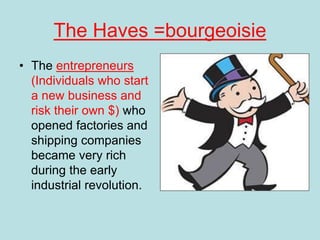
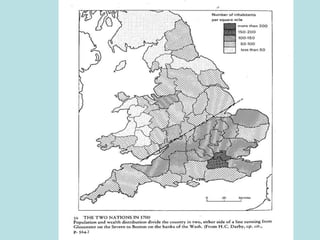
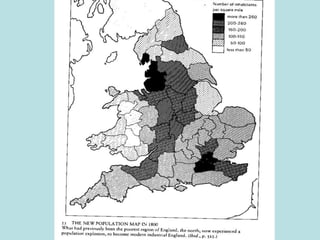
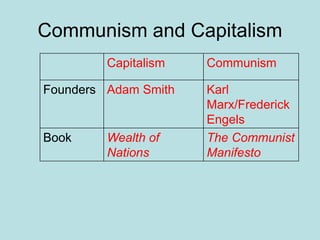
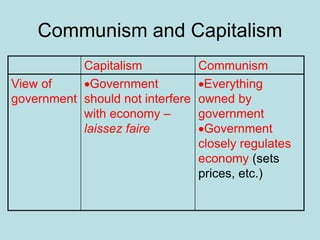
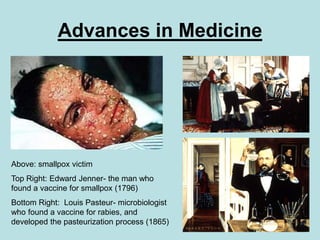
The Industrial Revolution transformed Britain from a largely agricultural society to an industrialized one between the late 18th and early 19th centuries. New technologies like the steam engine and mechanized textile manufacturing led people to move from rural areas to cities where factories were located. This rapid urbanization strained city infrastructure and living conditions, with overcrowded slums and poor sanitation. While factory owners profited, workers faced long hours, dangerous conditions, low pay, and few rights. The Revolution also brought new ideas about economics, politics, and society that still influence the modern world.