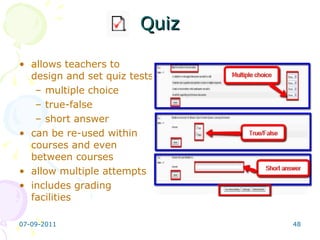
The document discusses Moodle, an open source learning management system (LMS). It provides an overview of Moodle's features and capabilities, including its modular design, interfaces for different user roles, and tools for structuring courses. It also outlines the basic steps for building a Moodle course, including choosing a format, adding content and activities, and configuring blocks. Common Moodle activities like forums, wikis and assignments are also described.
![E-Learning Technologies for Rural Development: Trends and Future Possibilities September 5-9, 2011 NIRD, Hyderabad Dr. Indira Koneru Online Course Facilitator Integrating Technology Website: http://wikieducator.org/User:Indkon E-mail: [email_address] Open Source LMS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indirammvc11-110928031754-phpapp01/85/Moodle-Open-Source-LMS-1-320.jpg)