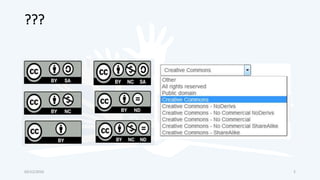
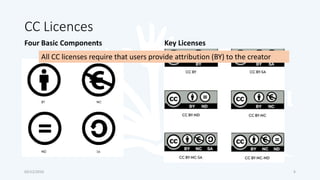
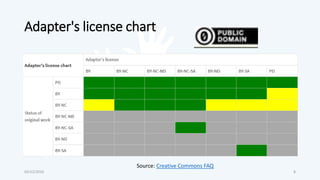
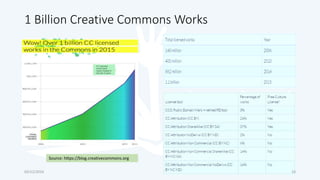
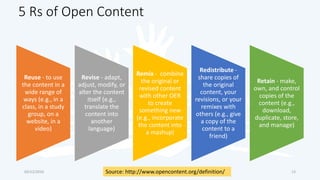
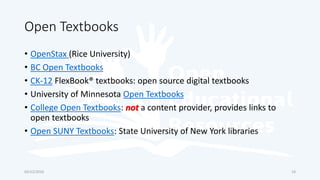
The document discusses open educational resources (OER) and Creative Commons (CC) licenses. It provides definitions of OER, explains the different types of CC licenses from most open to least open, and how they can be used to license educational content. It also outlines some key benefits of using OER, major sources of OER, and ways that educators can create and share their own OER.