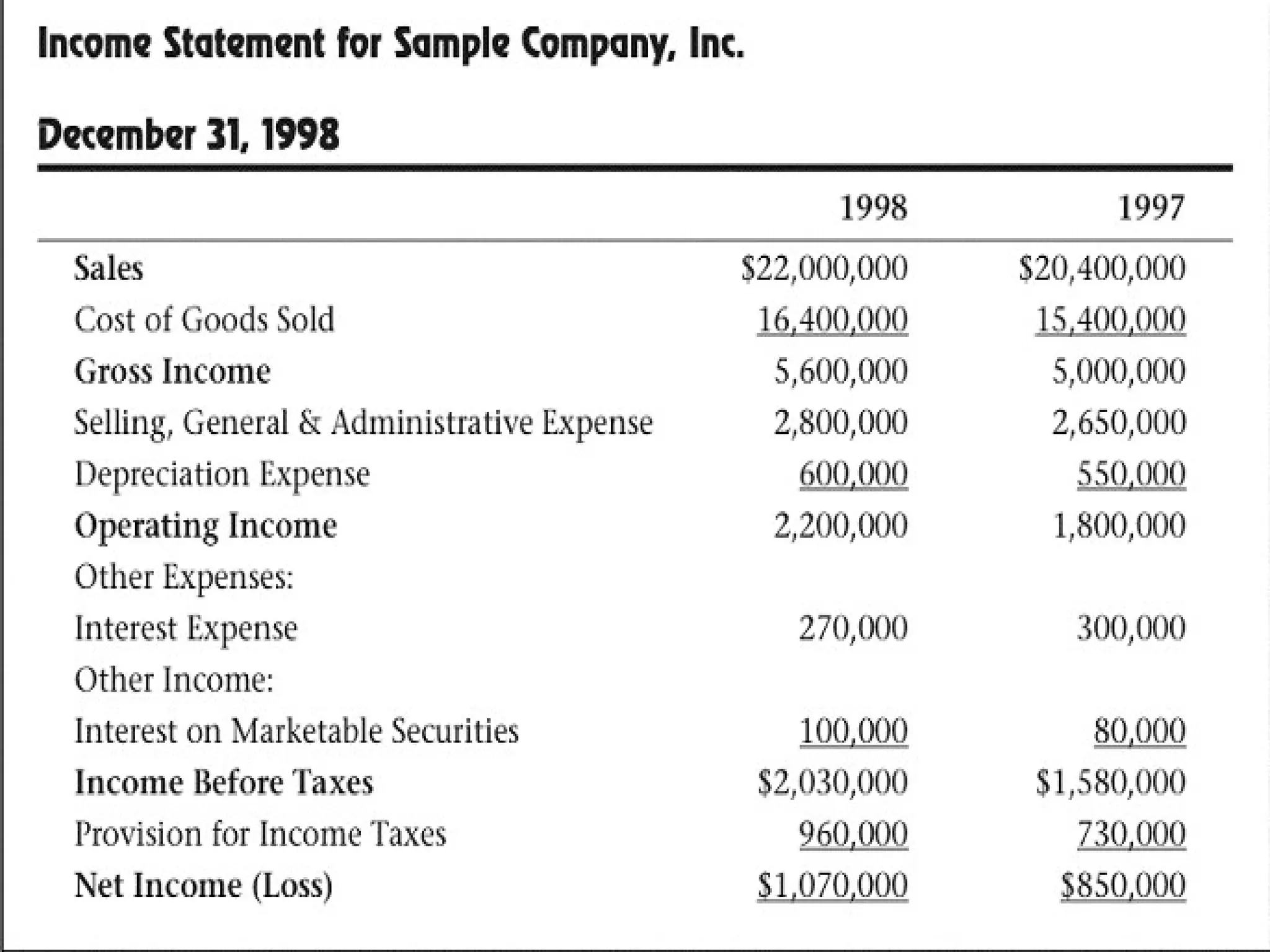
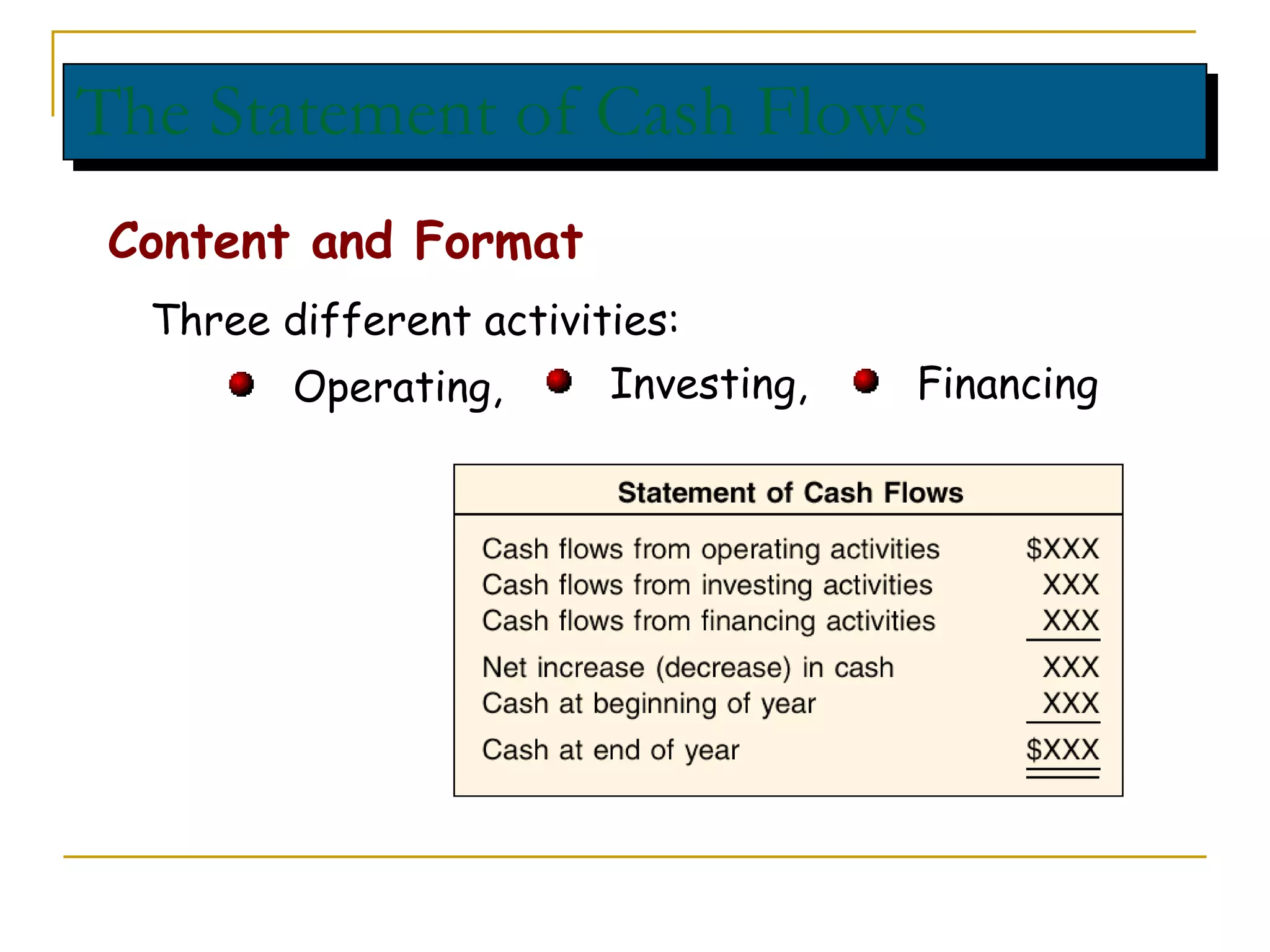
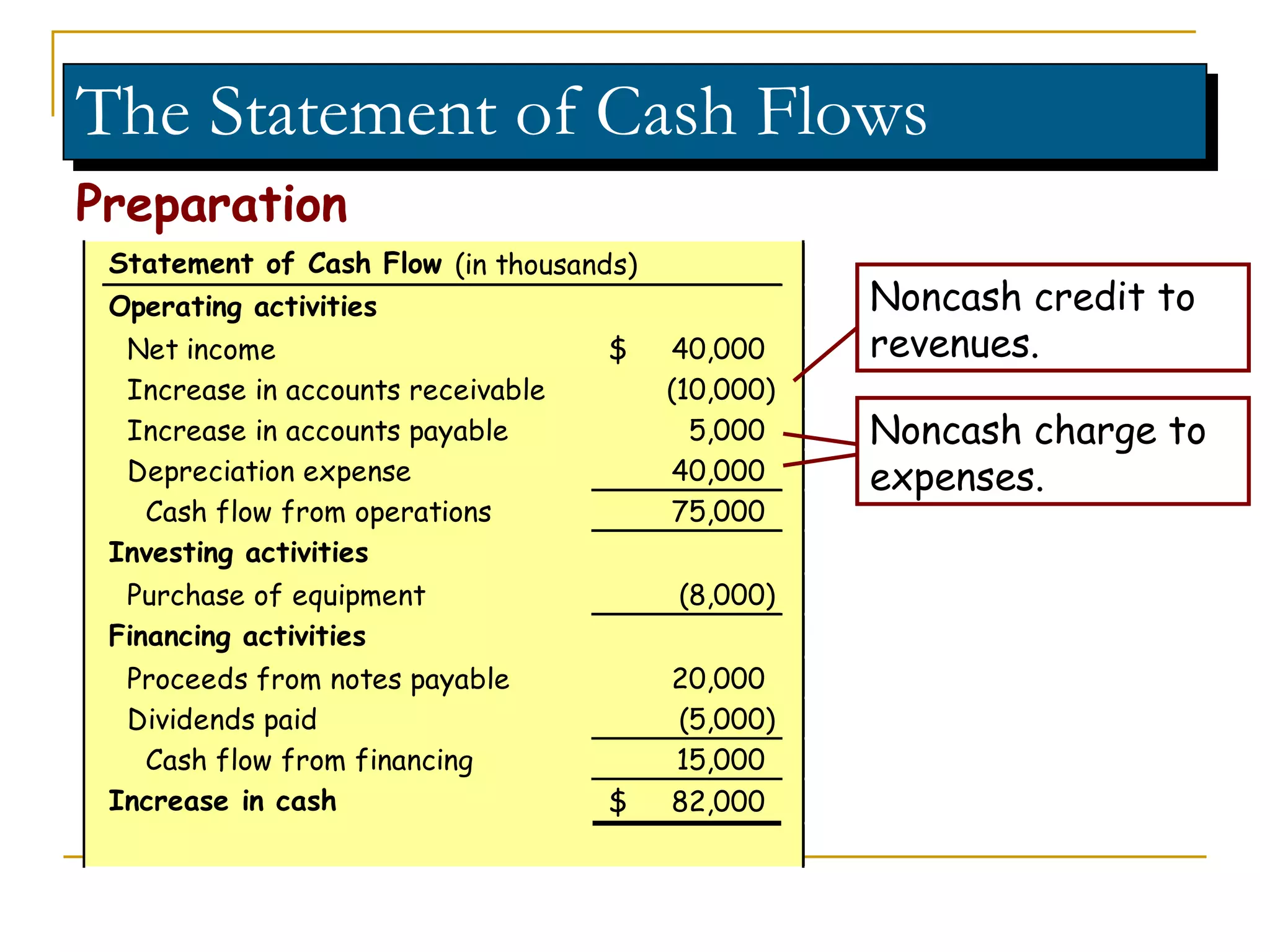
The document discusses income statements, cash flow, and the statement of cash flows. It defines income as earnings from operations, expenses as costs to earn income, and profit as income minus expenses. It explains that cash flow shows where cash came from and was spent, and the statement of cash flows categorizes these cash flows into operating, investing, and financing activities to evaluate a company's liquidity, solvency, and flexibility.