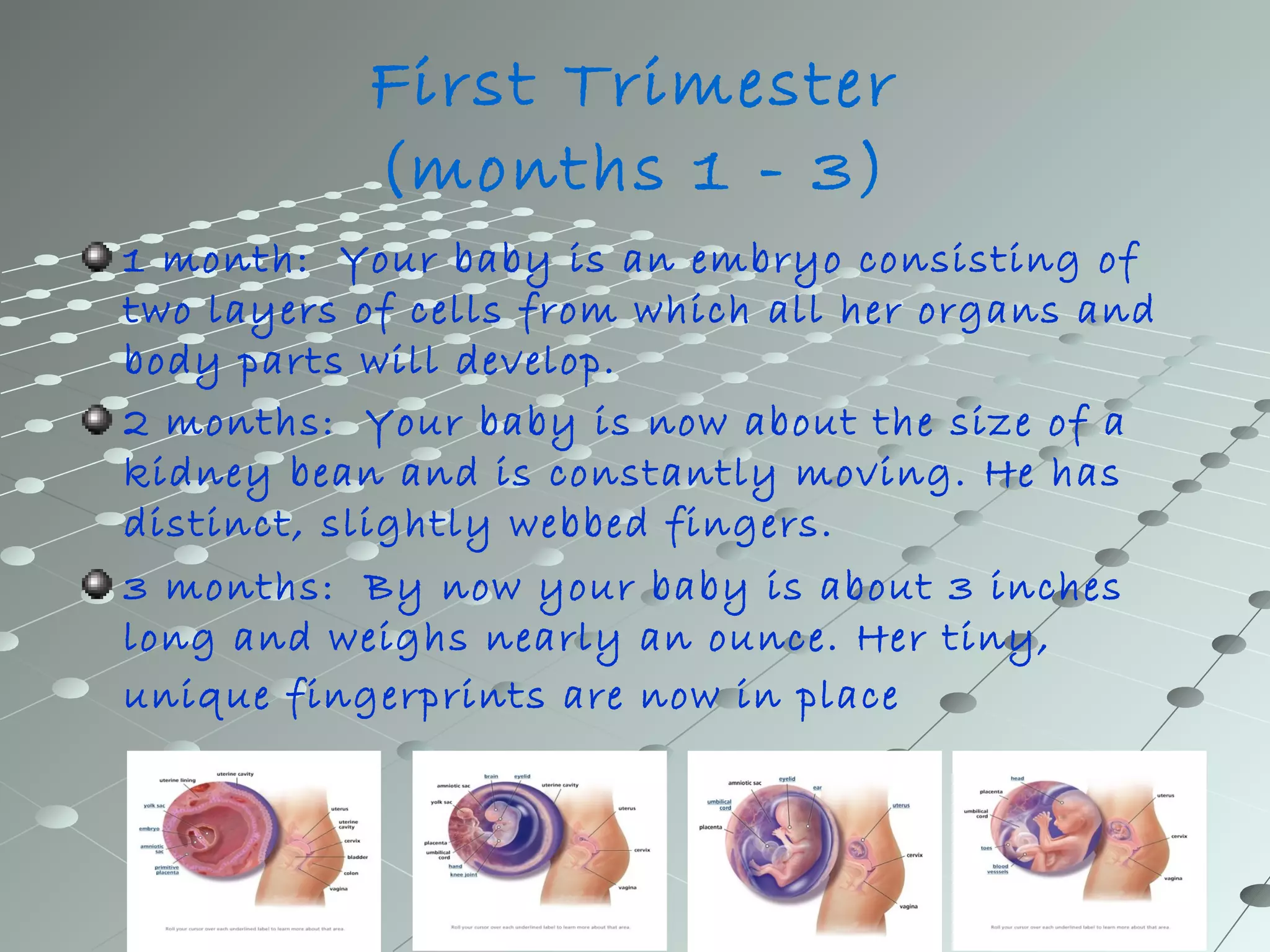
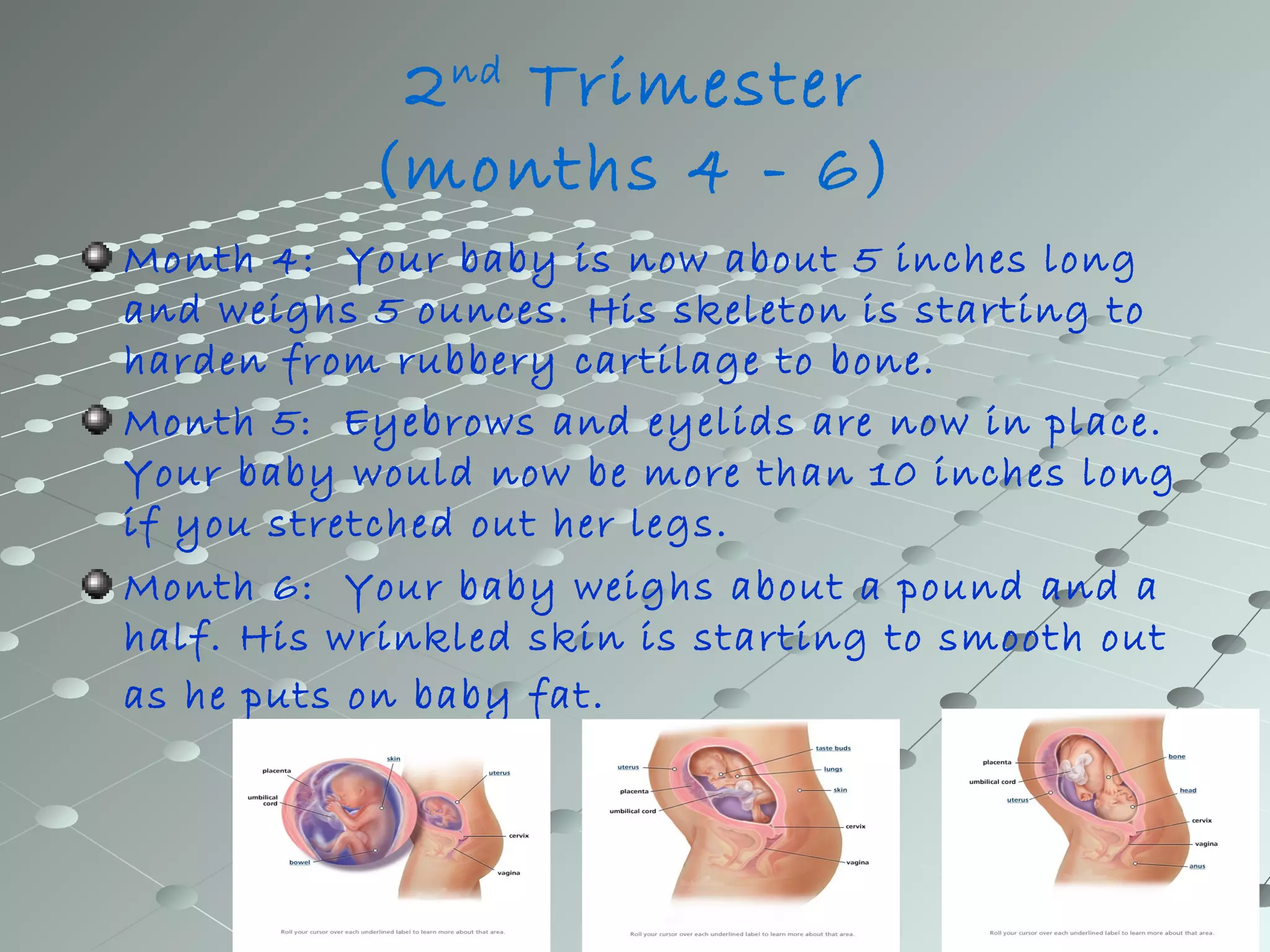
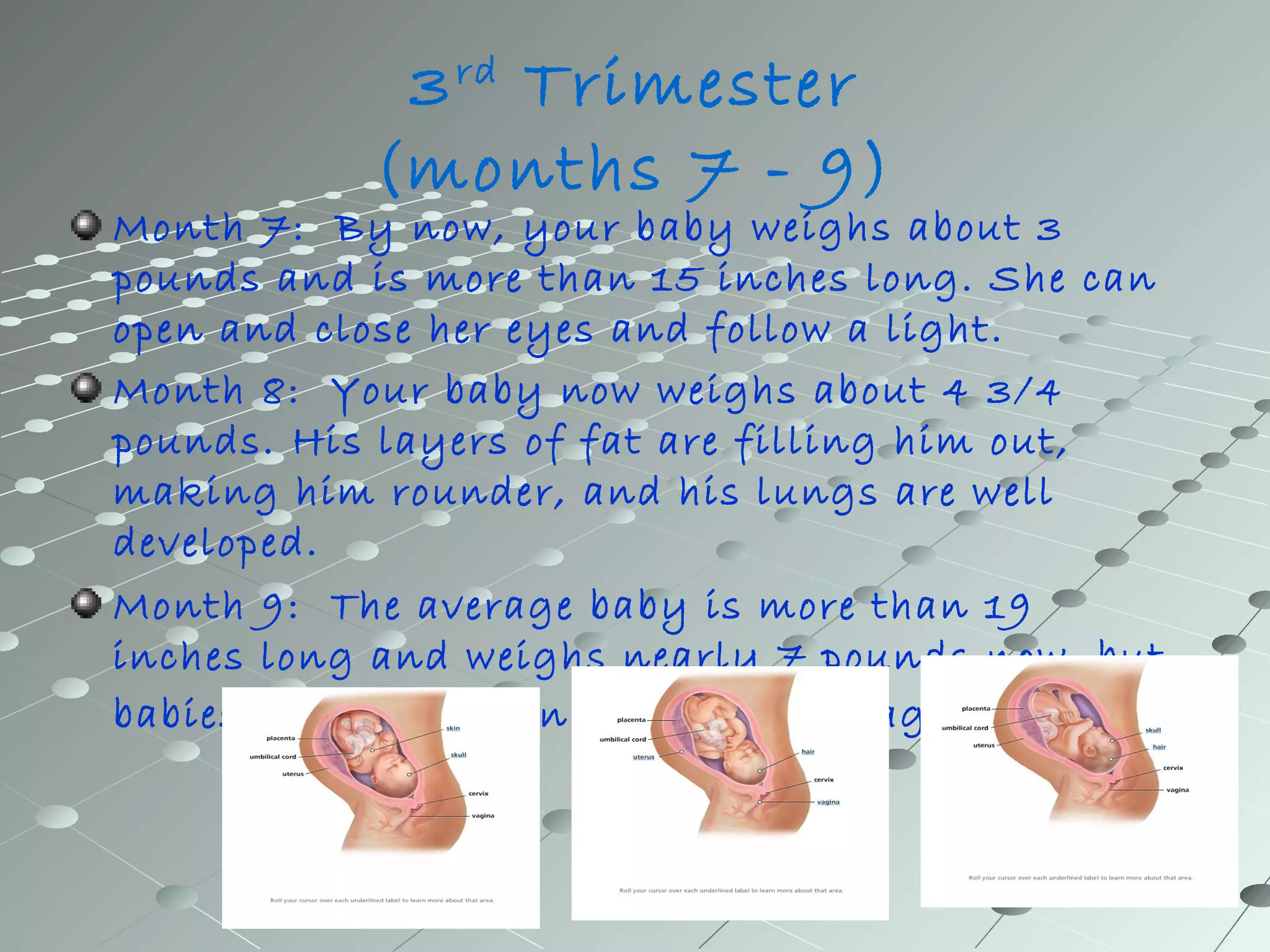
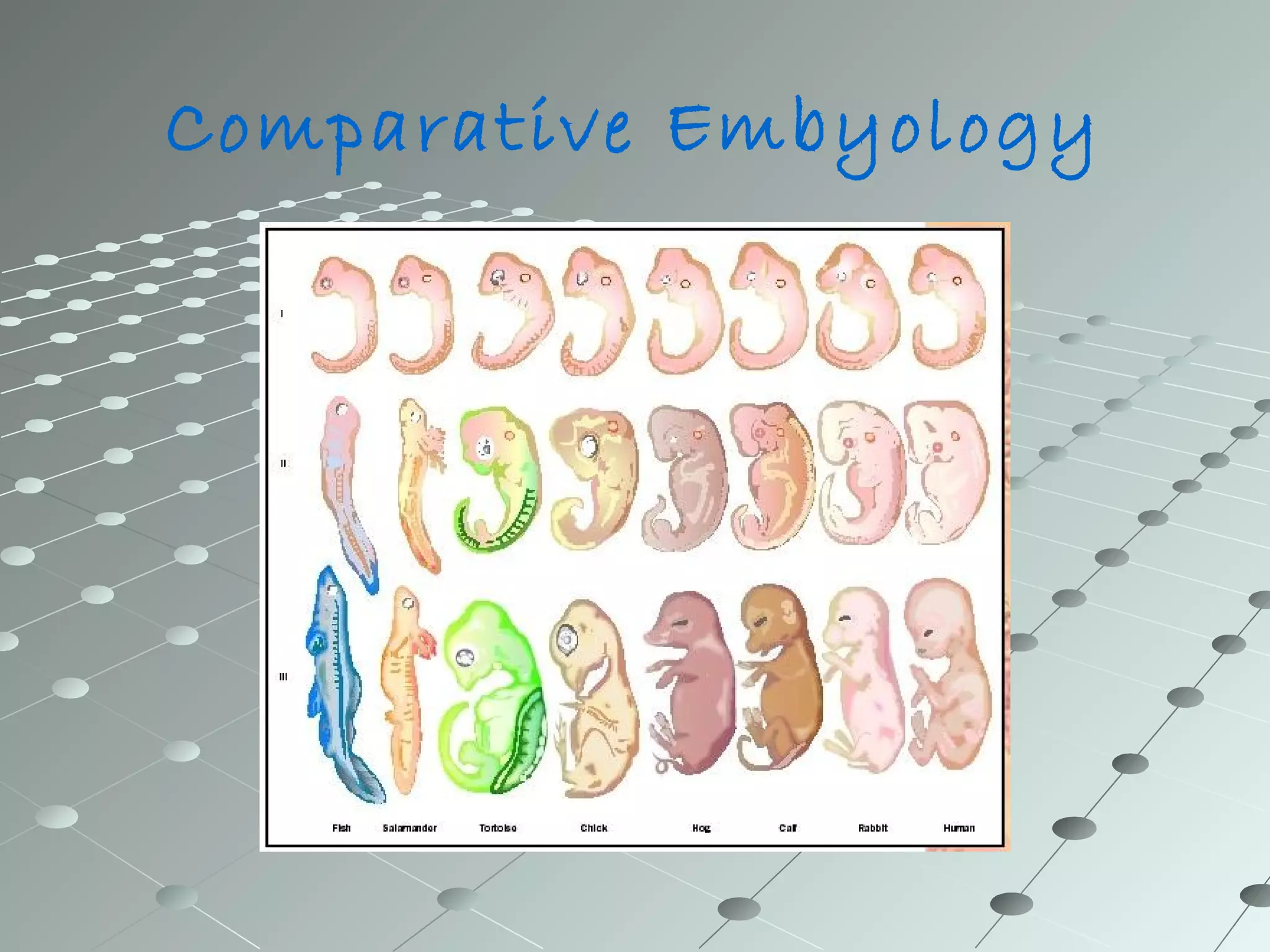
Human development from embryo to newborn occurs in three stages: the first, second, and third trimesters. In the first trimester, the embryo develops organs and body parts from two cell layers and fingerprints form. In the second trimester, the skeleton hardens and skin smoothes out. In the third trimester, organs continue developing and the baby gains weight and length. Comparative embryology shows that while human development is similar to other animals in its cell division and layer formation, it differs in the specific organs developed and whether development occurs inside or outside the mother's body, depending on the species.