During the first two weeks of development:
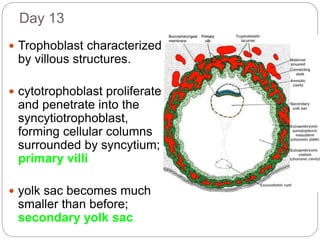
1) The trophoblast differentiates into the cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast layers, beginning primitive placental circulation.
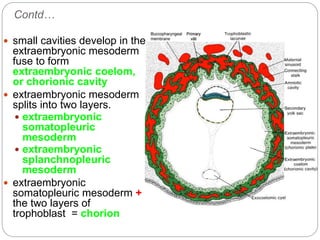
2) The embryoblast forms two layers, the epiblast and hypoblast, and the amniotic cavity develops over the epiblast.
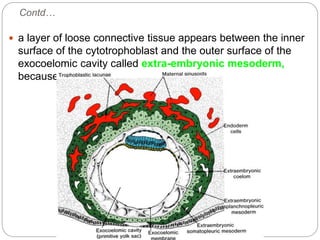
3) The extraembryonic mesoderm splits into the somatopleuric and splanchnopleuric layers between the trophoblast and embryo.
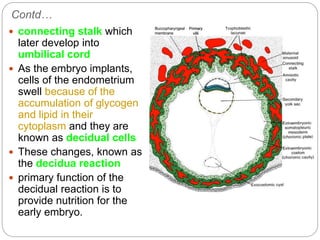
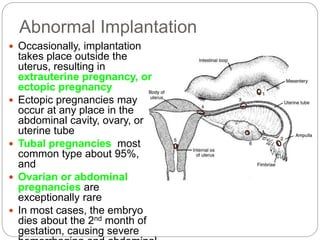
Implantation is usually complete by the end of the second week, though abnormal implantation can occur outside the uterus, risking ectopic pregnancy.