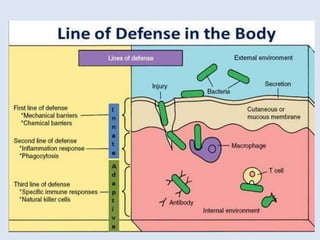
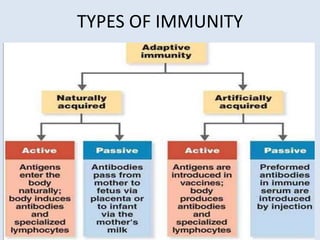
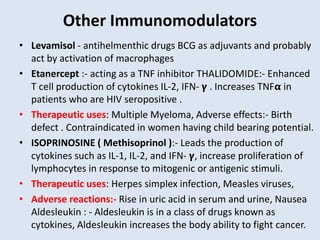
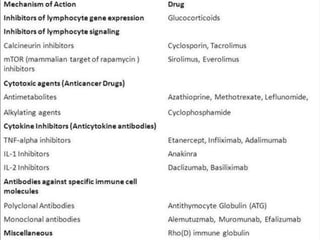
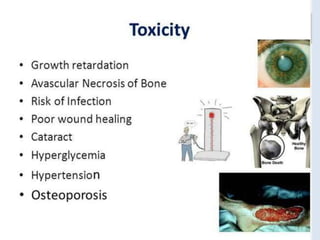
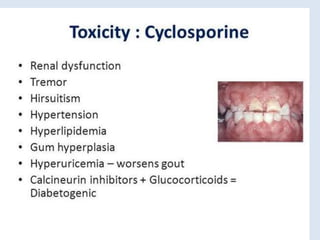
The document discusses various immunomodulators and their roles in the immune system, detailing types of immunity, therapeutic uses, and adverse effects. It highlights the functions of cytokines, immunostimulants, glucocorticoids, calcineurin inhibitors, anti-TNF agents, and other immunomodulating drugs in treating diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and transplant rejection. Additionally, it explains the mechanisms of action of these agents and their implications for patient care.