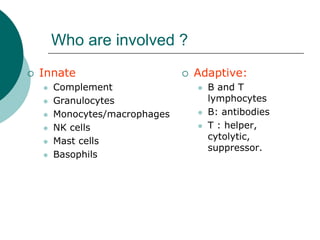
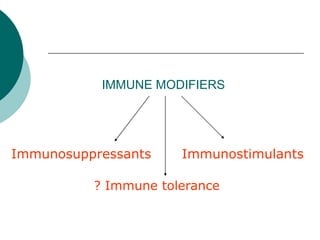
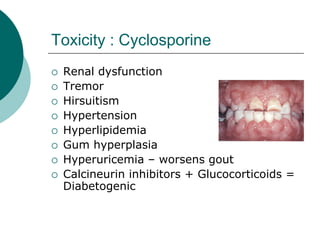
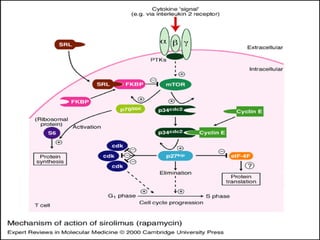
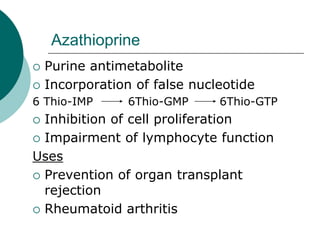
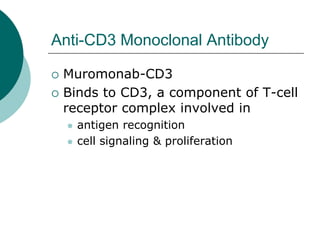
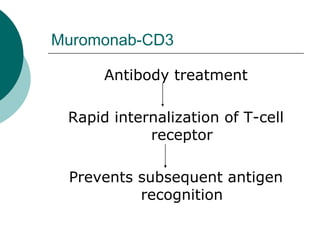
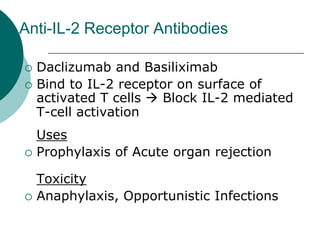
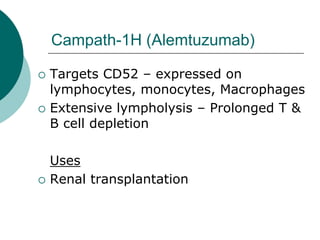
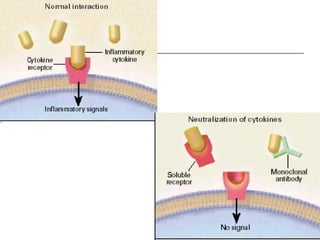
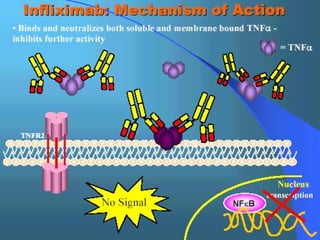
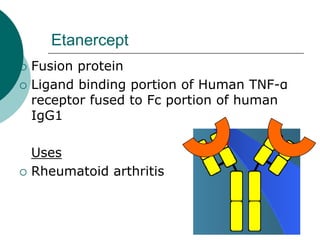
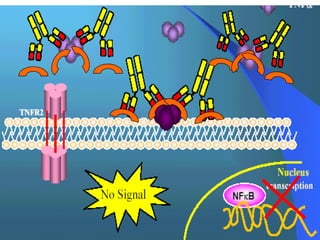
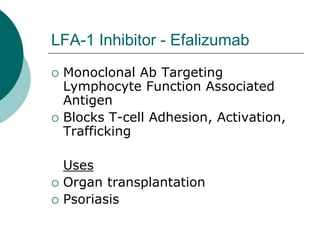
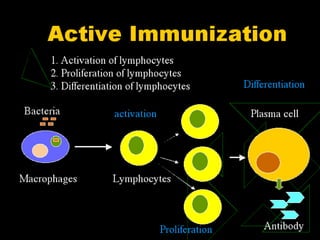
The document discusses various aspects of immunopharmacology including the immune response, cells involved, immune modifiers, and immunization approaches. It describes several classes of immunosuppressive drugs like glucocorticoids, calcineurin inhibitors, antiproliferative agents, antibodies, and their mechanisms and uses. Some immunostimulants like levamisole, thalidomide, BCG, interferons, interleukin-2 are also mentioned along with their effects. The summary concludes with a brief overview of active and passive immunization approaches including vaccines, immune globulins, and Rho(D) immune globulin.