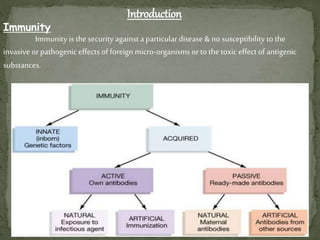
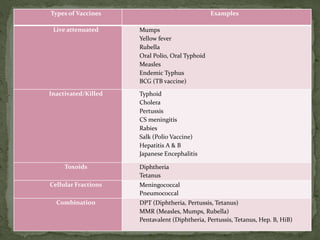
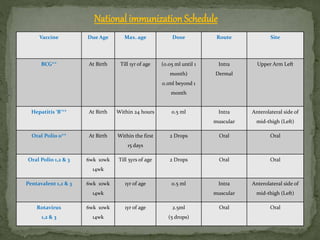
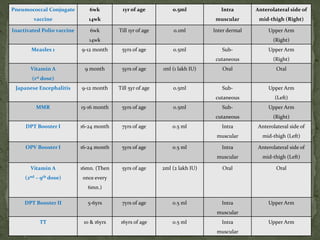
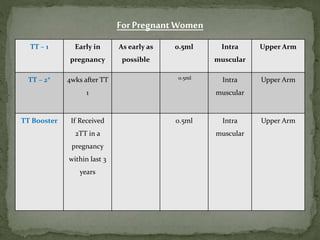
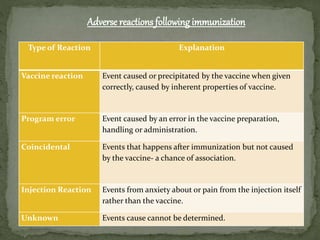
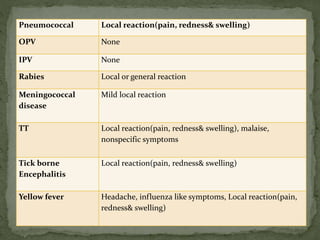
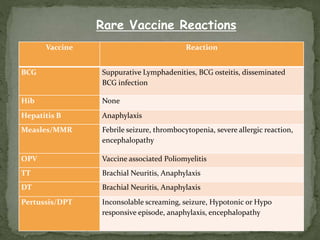
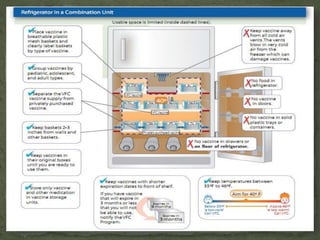
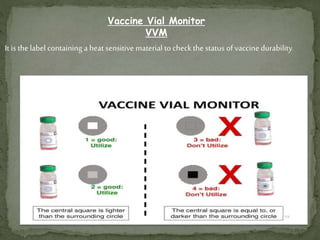
The document provides a comprehensive overview of immunization, including definitions of immunity and immunization processes, types of vaccines, and their classifications. It details the National Immunization Programme in India and the schedules for various vaccines, as well as vaccine storage, cold chain management, and reactions to vaccinations. Additionally, it highlights the importance of immunization in reducing child mortality and promoting public health.