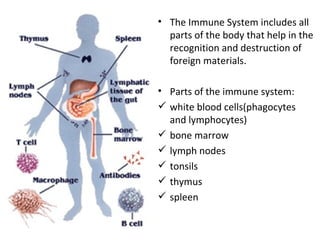
The document explains the immune system's role in defending the body through various defense mechanisms, including the first line (skin, sweat, tears, etc.), second line (phagocytosis and inflammatory response), and third line (specific immune response). It outlines key terminology such as antibodies, antigens, immunity, and vaccination, as well as types of immunity (passive and active) and related immune system disorders like hay fever and asthma. Additionally, it details the processes by which the body recognizes and responds to pathogens, emphasizing the importance of specialized cells and antibodies.