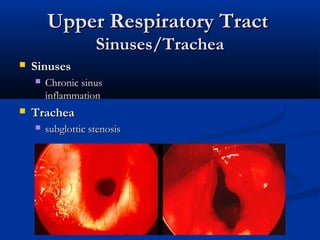
This document summarizes Wegener's granulomatosis (WG), a rare disease characterized by inflammation of blood vessels. In the 1930s it was first described by Friedrich Wegener based on patients exhibiting necrotizing granulomas in the respiratory tract and inflammation of blood vessels throughout the body. Diagnosis is based on clinical criteria including nasal or oral inflammation, lung abnormalities on chest imaging, kidney involvement, and granulomatous changes on biopsy. Pathogenesis involves antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) that activate neutrophils, causing tissue damage. WG commonly affects the upper respiratory tract, lungs and kidneys. Treatment involves immunosuppressive medications like glucocorticoids and cyclophosphamide