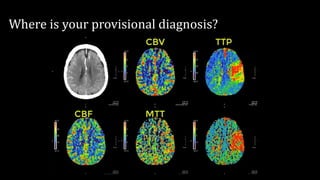
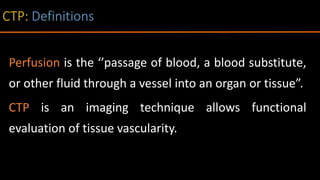
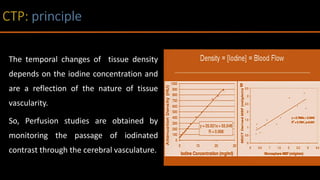
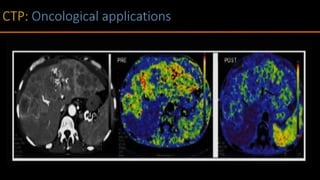
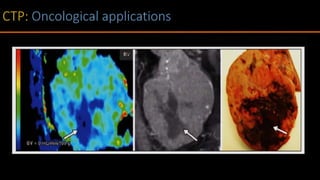
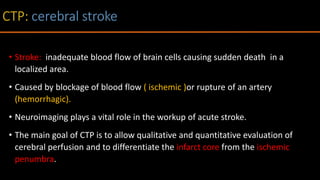
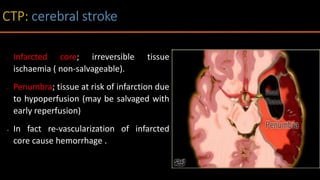
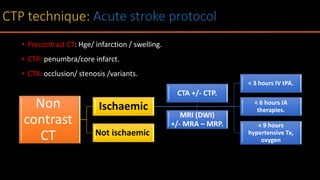
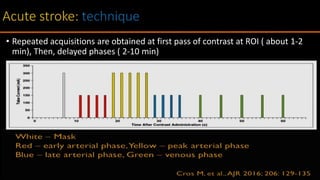
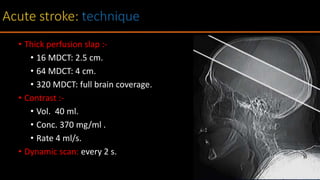
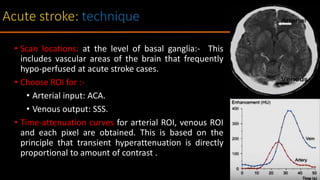
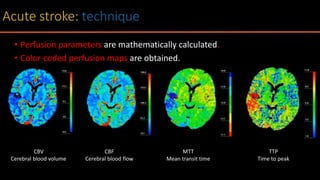
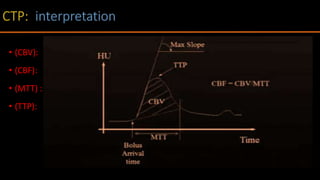
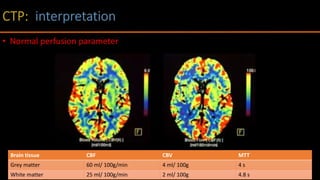
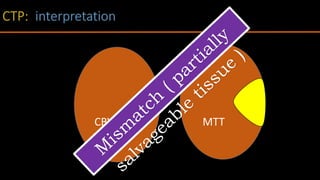
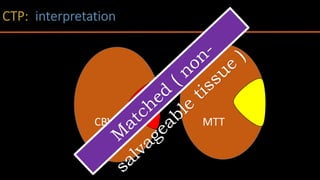
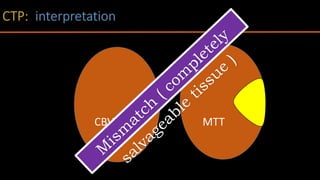
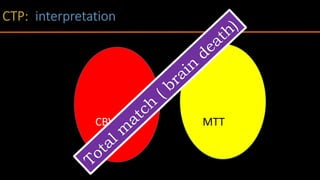
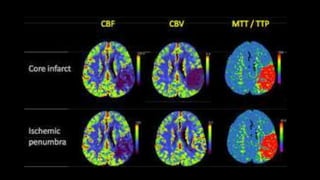
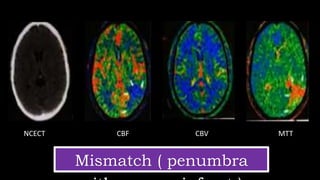
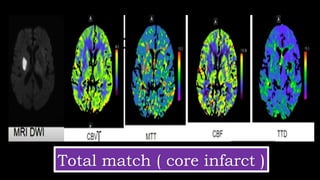
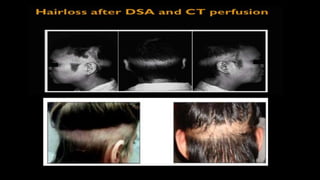
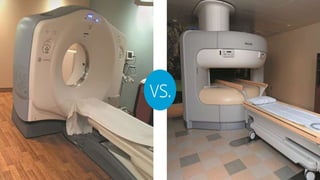
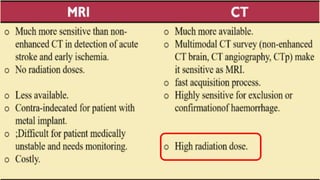
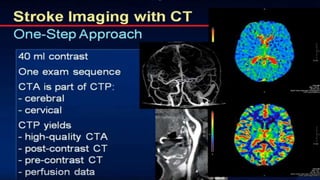
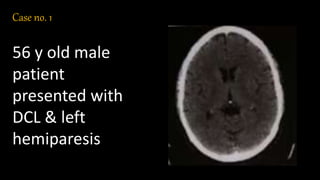
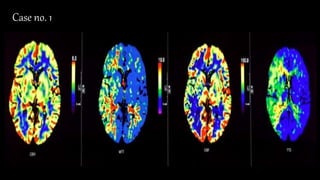
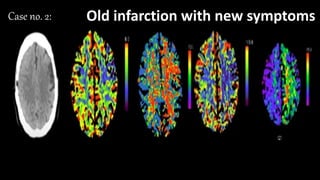
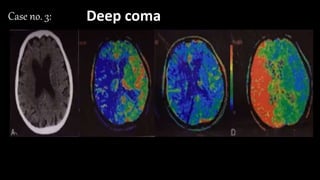
The document discusses the use of Computed Tomography Perfusion (CTP) for evaluating tissue vascularity in various medical conditions, particularly acute cerebral stroke and oncological applications. It highlights the importance of perfusion studies in differentiating infarcted tissue from salvageable brain areas and outlines the specific perfusion parameters including cerebral blood volume (CBV), cerebral blood flow (CBF), mean transit time (MTT), and time to peak (TTP). Additionally, it addresses the limitations of CTP, such as radiation exposure, and provides case studies illustrating the diagnostic process.