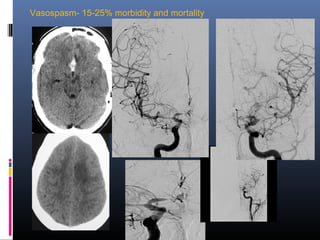
1) Neurovascular diseases like stroke are a major cause of death and disability worldwide. Advances in neuroimaging and endovascular neurointerventions now allow minimally invasive treatments for conditions like aneurysms and acute ischemic strokes.
2) Recent clinical trials have shown the benefits of endovascular therapies like stent retrievers for acute ischemic stroke. This represents a dramatic change in stroke management from older failed trials testing earlier devices.
3) A neurointerventionist, neurologist, neurosurgeon and radiologist working as a integrated team is key to utilizing the latest minimally invasive treatments for various neurovascular conditions like aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations and carotid artery stenosis.