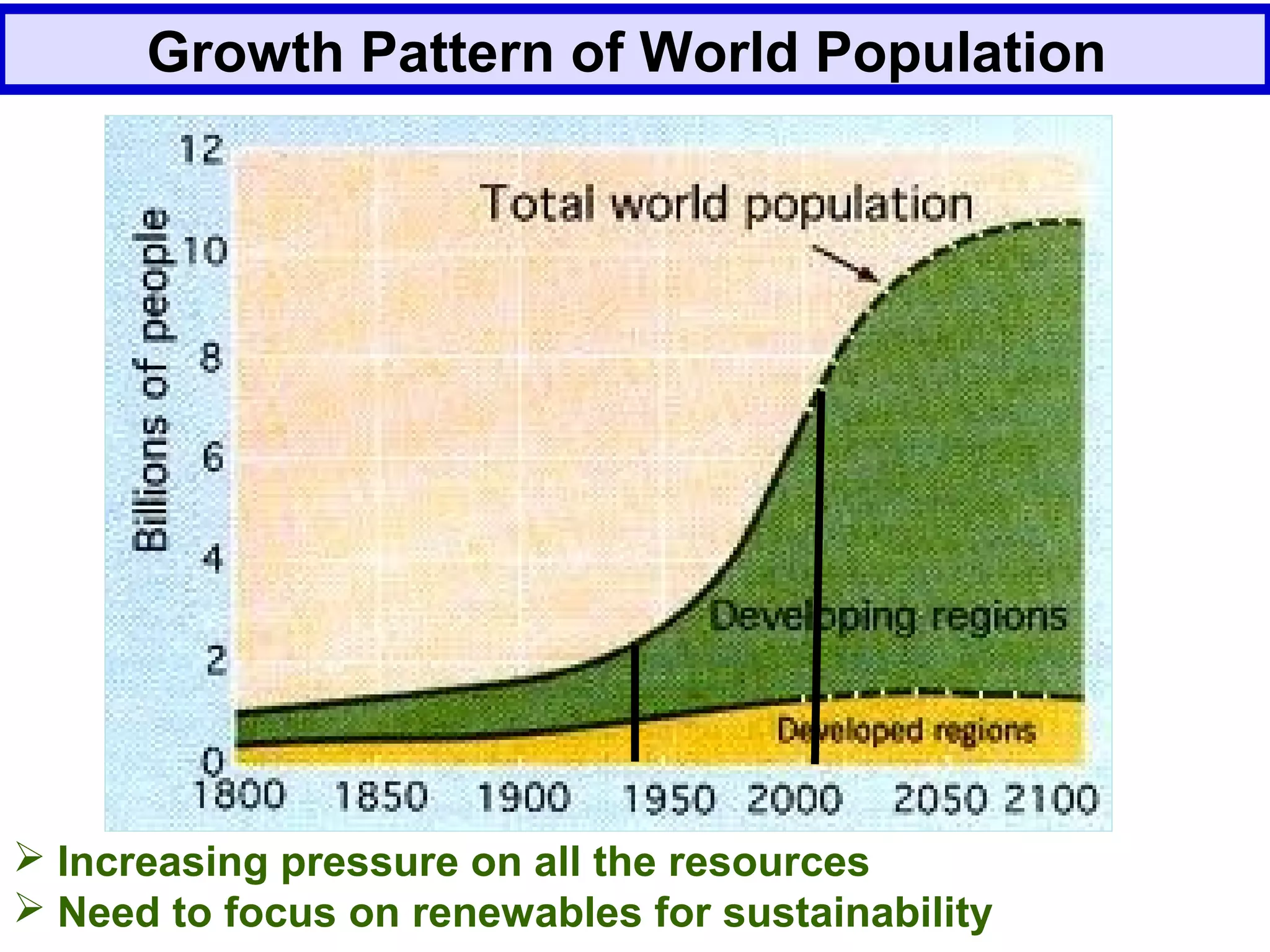
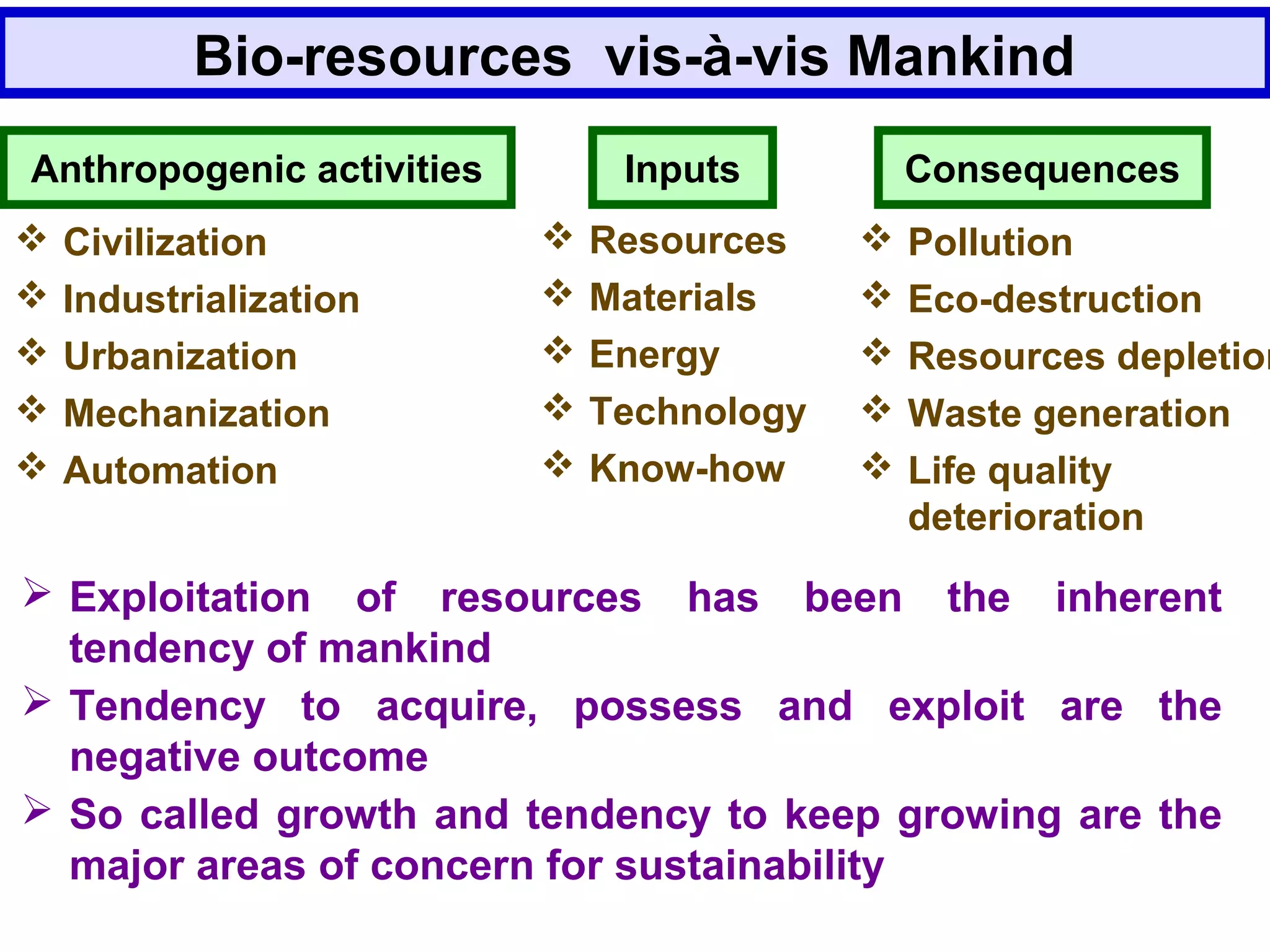
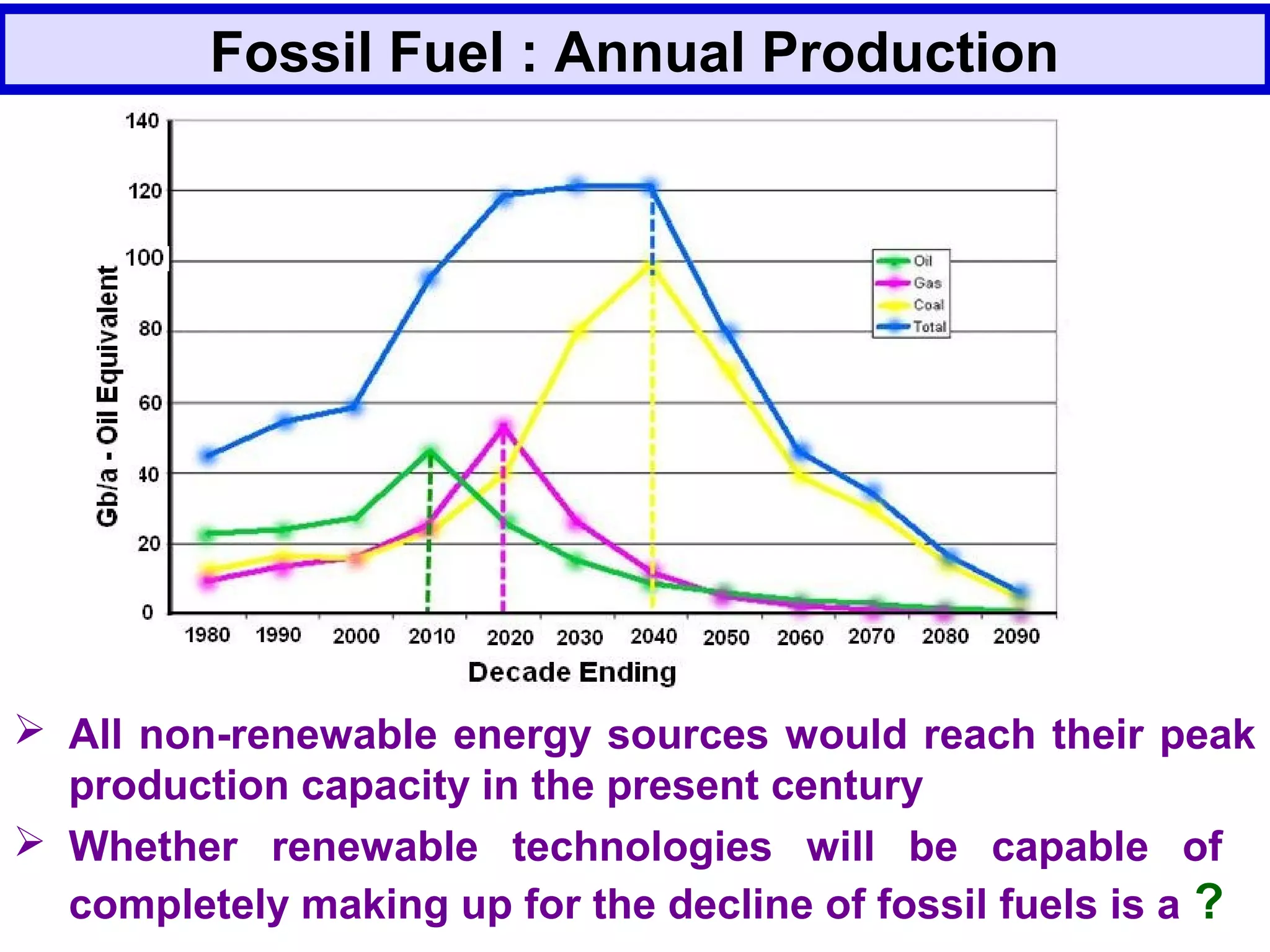
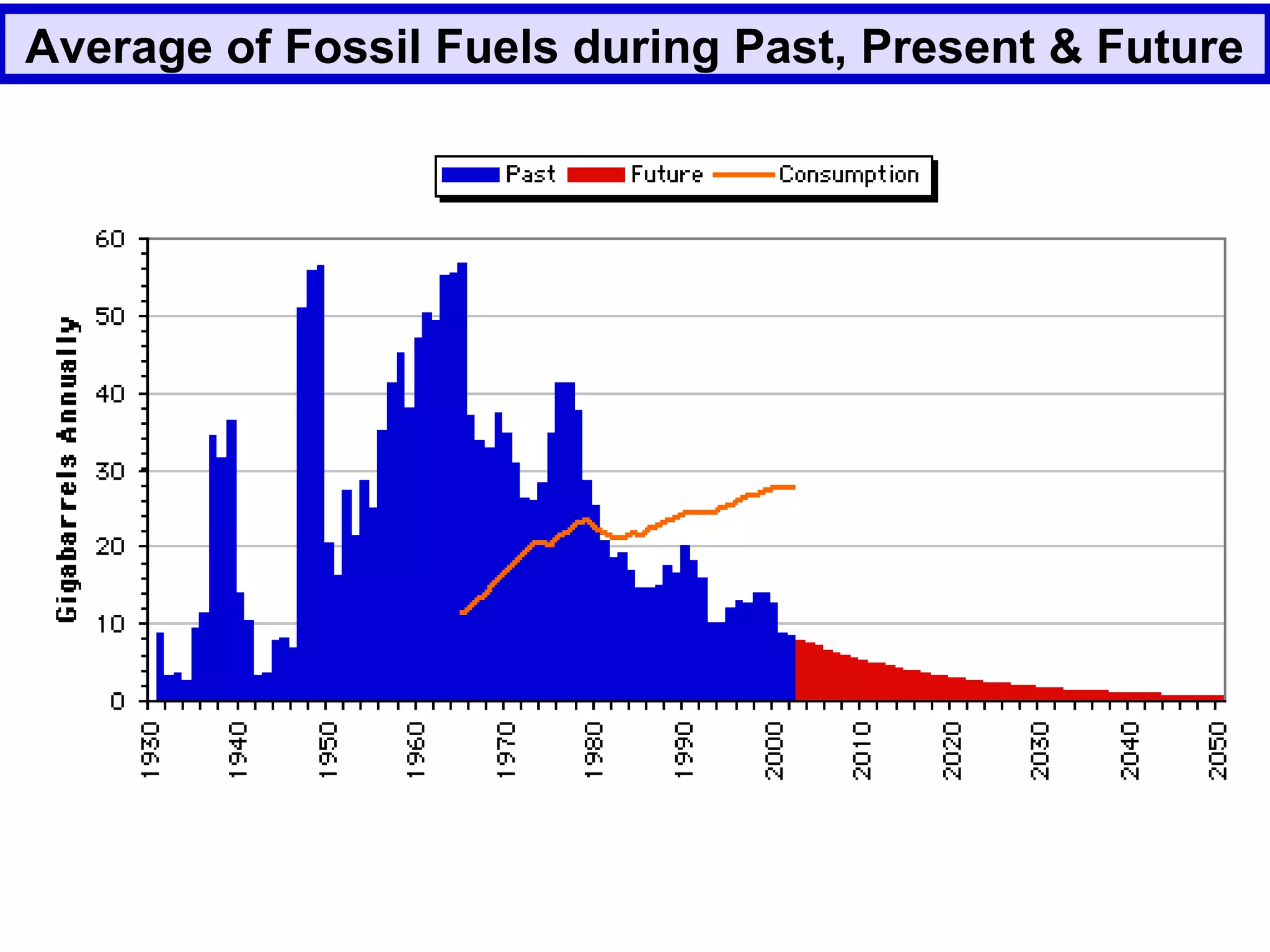
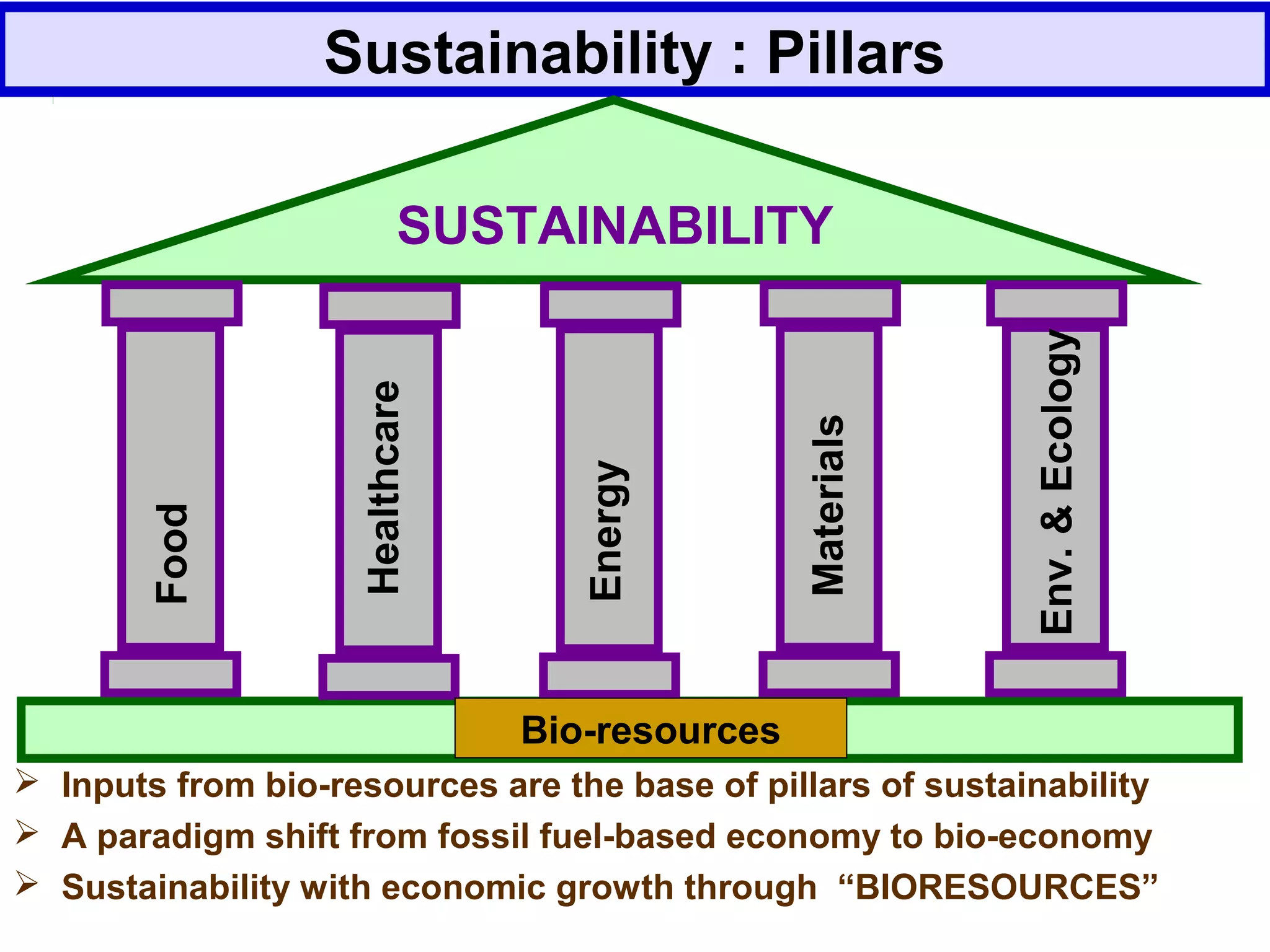
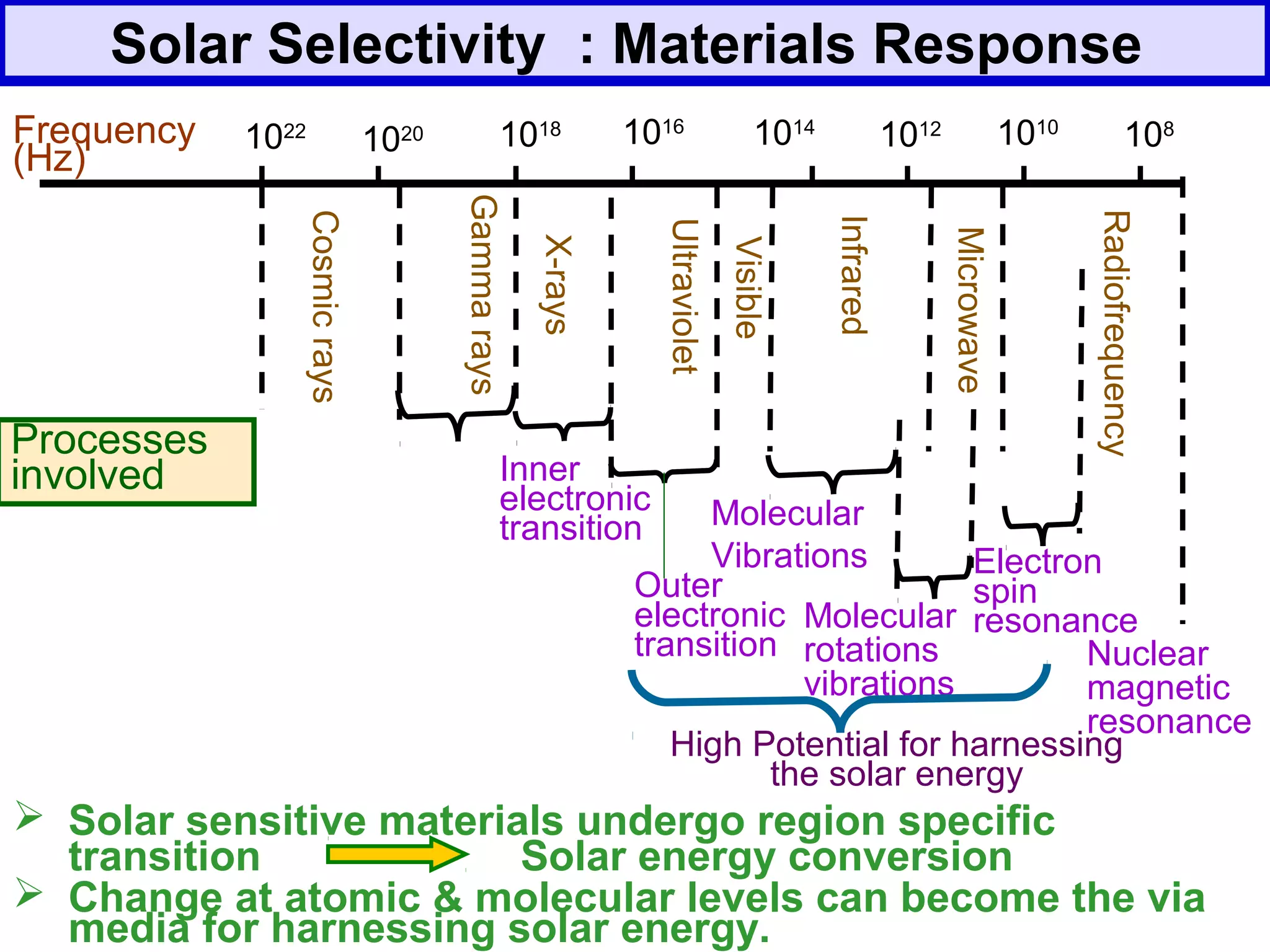
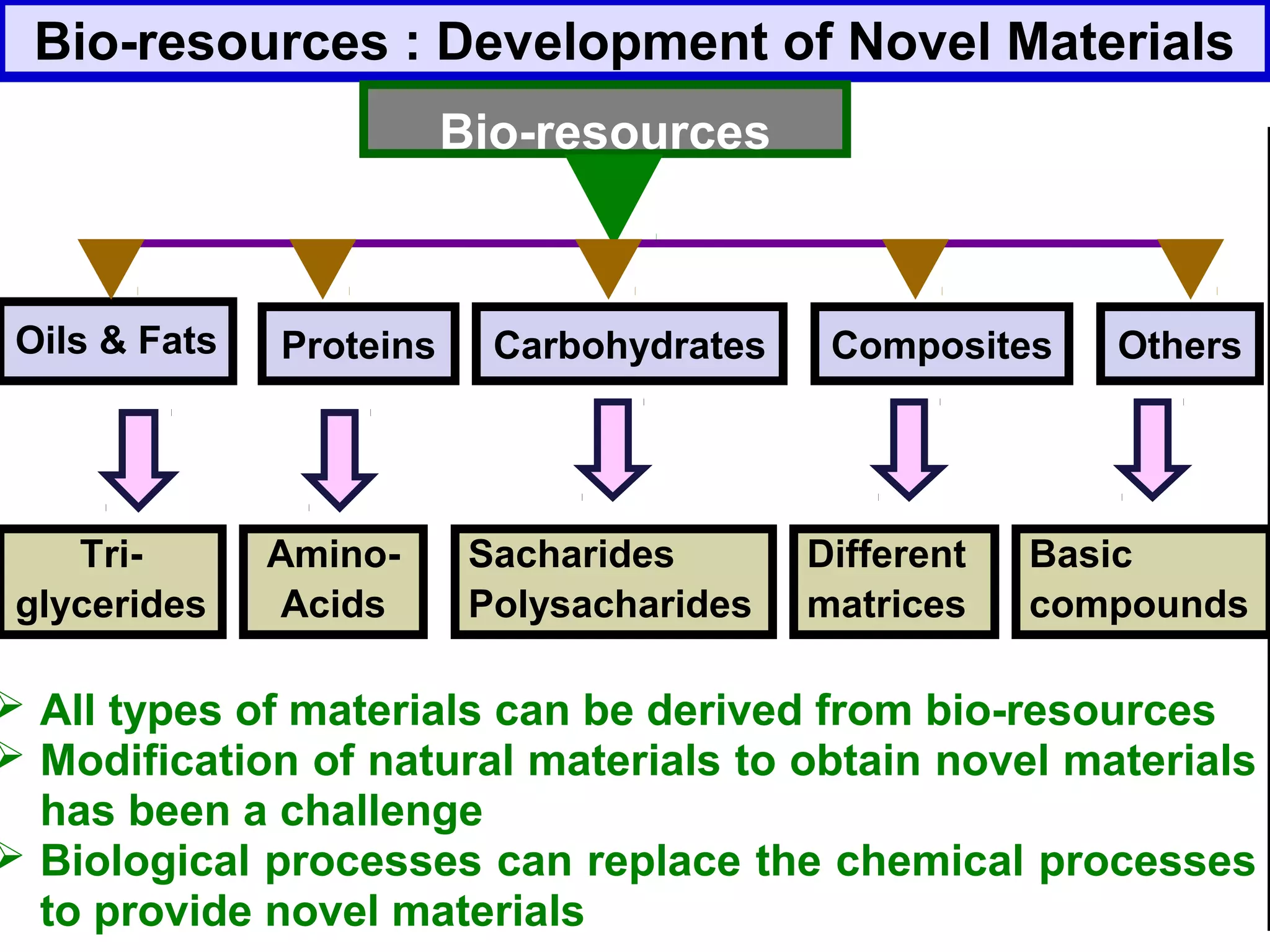
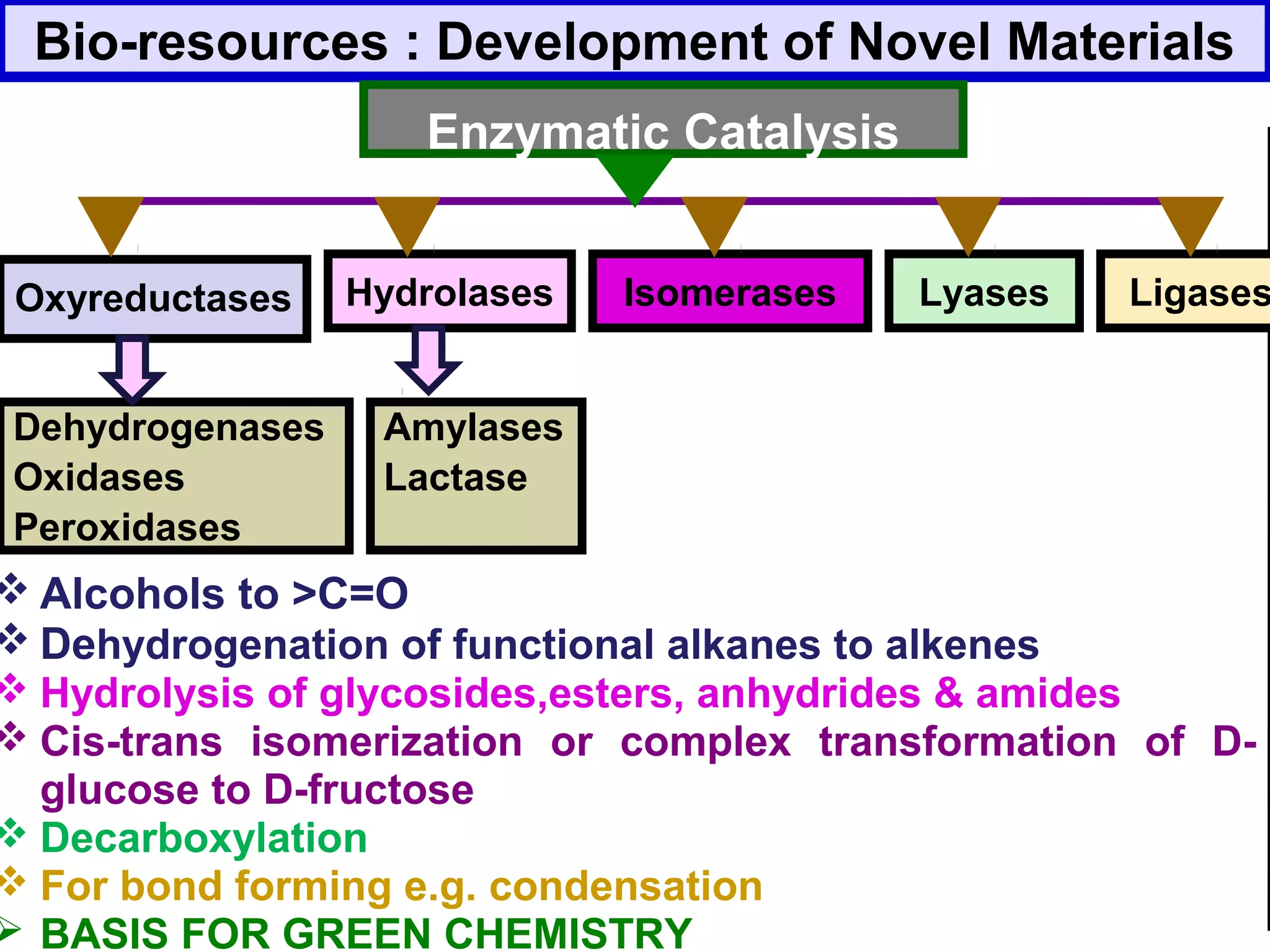
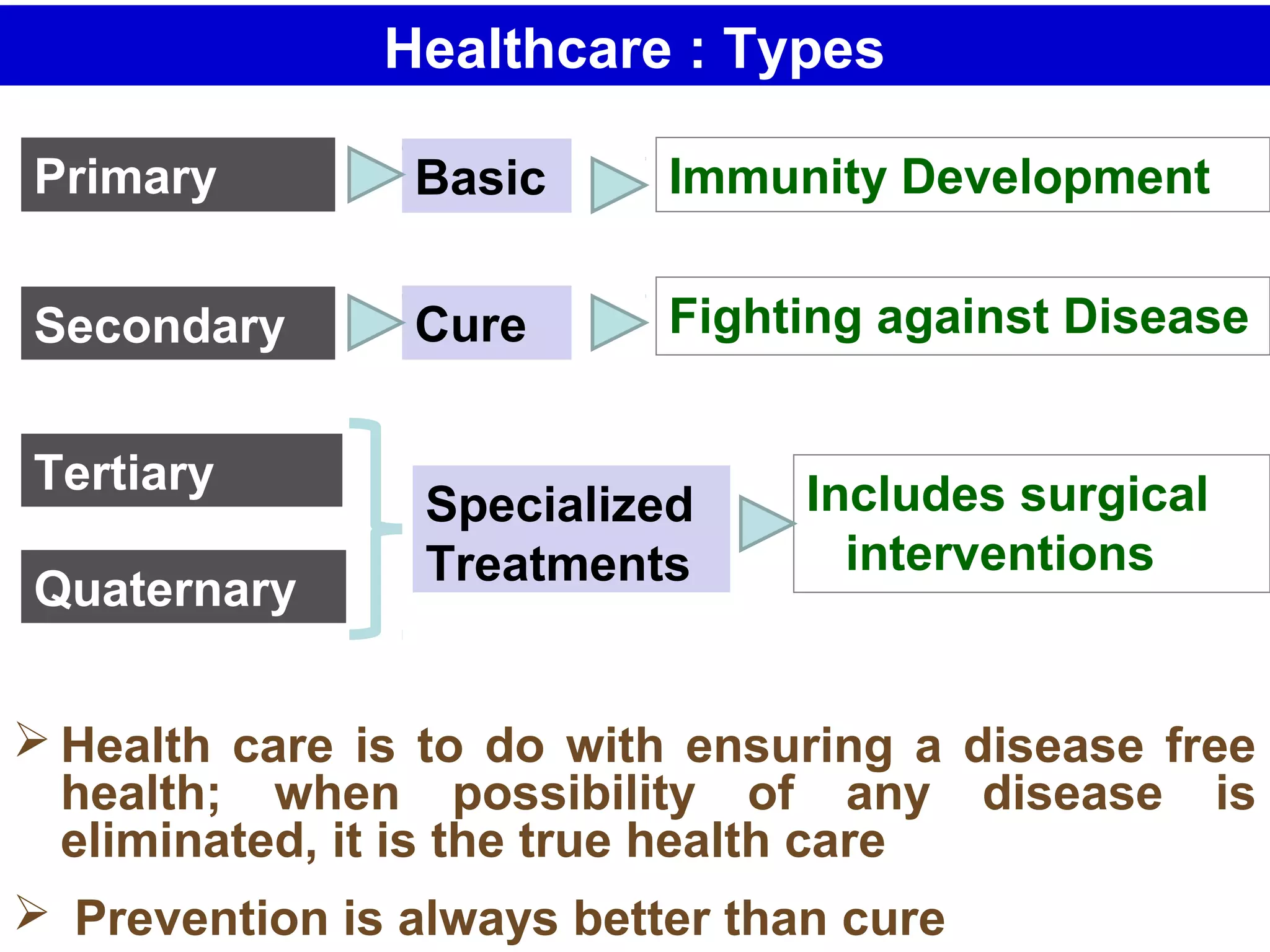
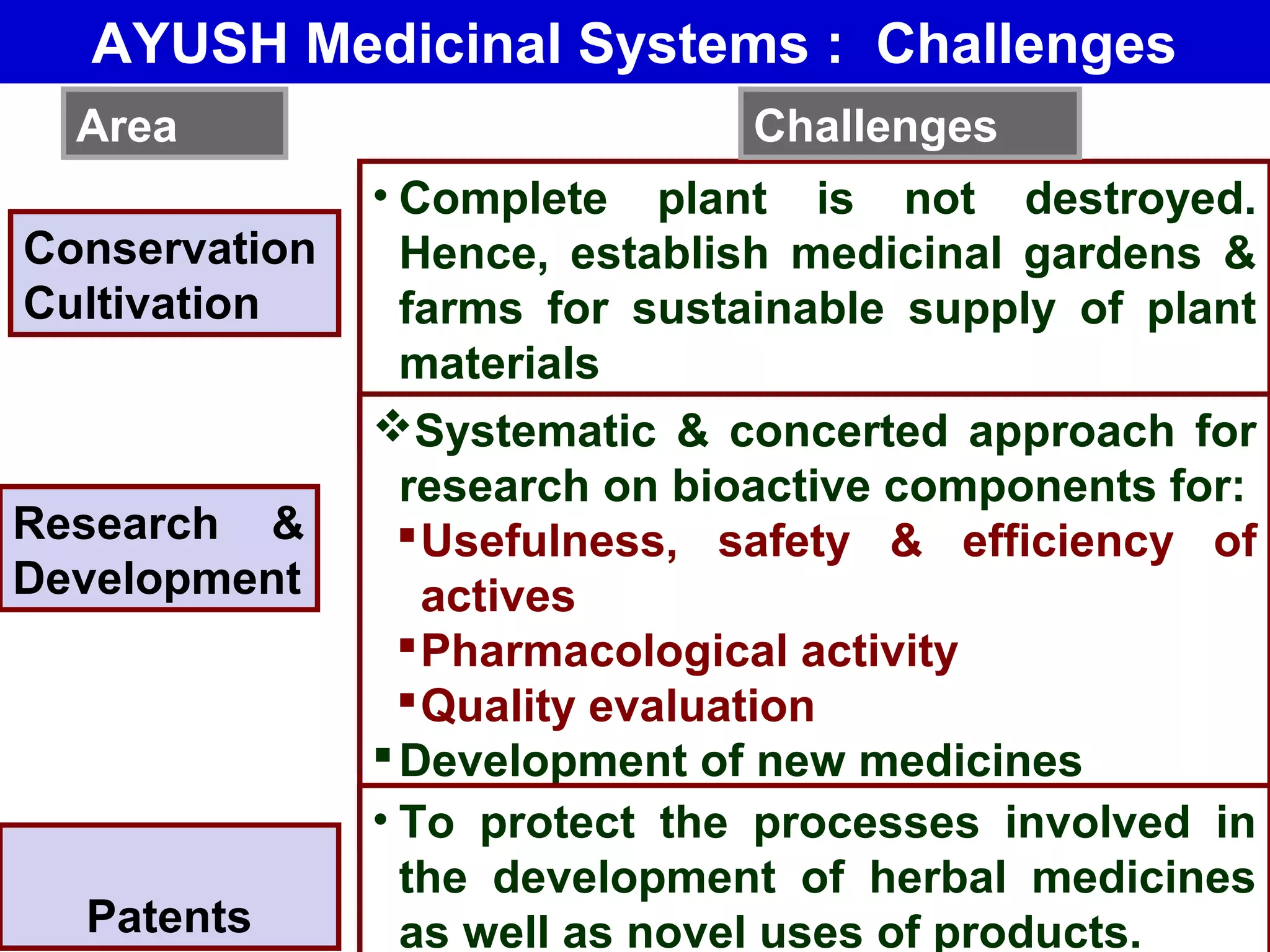
The document discusses the potential of bio-resources for sustainable growth. It notes that with increasing population pressure on resources, there is a need to focus on renewables like bio-resources for sustainability. It defines sustainability as meeting present needs without compromising future generations' ability to meet their own needs. Some of the key challenges to sustainability include rapid population growth, depletion of natural resources, and increasing pollution levels. The document argues that exploitation of bio-resources can help provide pillars for sustainability in areas like energy, food, healthcare, and materials. It also discusses various attributes, drivers, and requirements for the sustainable utilization of bio-resources.