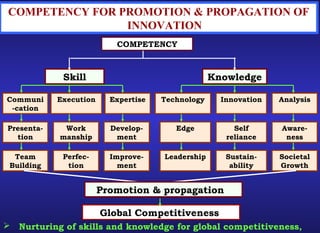
This document outlines key aspects of innovation and technology. It discusses defining innovation, dimensions of innovation including ordinary and extraordinary types. It describes the steps involved in innovation including initiation, idea generation, evaluation and implementation. Driving forces for innovation that promote competitiveness are also presented. The document then covers technology, the approach dynamics of technology including inputs, processes, outputs and transfer. It concludes by discussing the important components of a technology package including feasibility, economic viability, know-how, room for innovation and environmental sustainability.