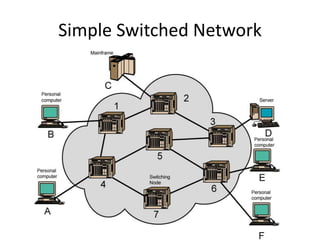
This document discusses different types of switching techniques used in internetworks. It describes circuit switching and packet switching as the two broad categories of switching.
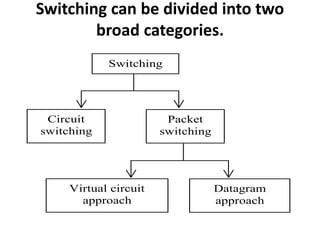
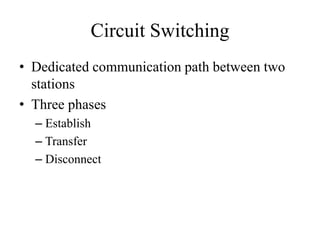
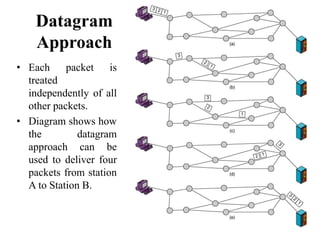
Circuit switching establishes a dedicated communications channel between two stations in three phases: establish, transfer, and disconnect. Packet switching can use either a datagram or virtual circuit approach. The datagram approach treats each packet independently by routing them from source to destination. The virtual circuit approach pre-plans a route for packets to follow from source to destination.
The document also discusses IP addressing methods and different classes of IP addresses including Class A, B, C, and D. It describes an activity for students to discuss the drawbacks of each IP address class.