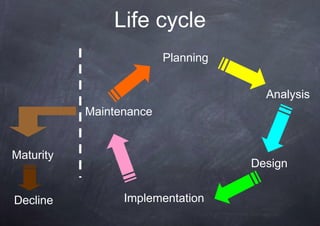
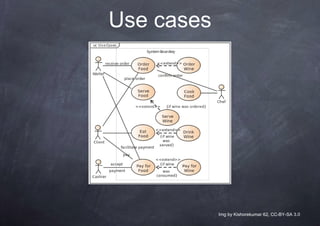
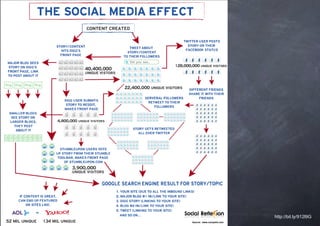
The document outlines a course program on setting up startups in Italy, covering key topics like startup regulation, business models, funding options, and project design. It emphasizes the importance of planning, teamwork, feasibility studies, and communication in launching a successful startup. Additionally, it discusses the role of business incubators and seed accelerators in supporting new ventures.