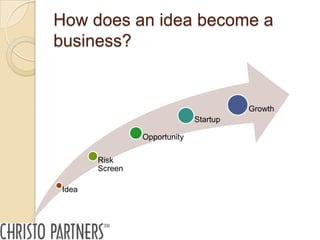
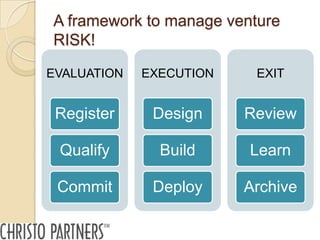
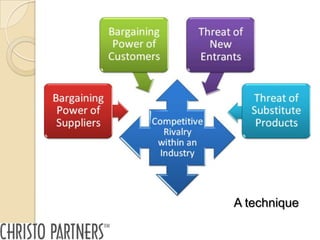
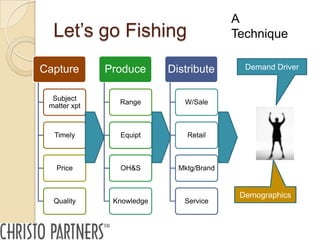
The document outlines a pitching workshop led by Peter Christo, focused on evaluating how ideas evolve into businesses by managing risks and identifying commercial opportunities. It emphasizes the importance of a clear value proposition, understanding market demand, and developing a coherent business model, along with key questions for screening ideas. Additionally, it provides guidance on effectively pitching these ideas to various stakeholders while considering the essential criteria for successful presentations.